Thymosin Alpha-1
A 28‑amino‑acid thymic peptide (thymalfasin) associated with immune modulation.
Key Research Properties:
| SKU: | thymosin-alpha-1 |
|---|---|
| Purity: | >99% (HPLC Verified) |
| Form: | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C |
| CAS Number: | 62304-98-7 |
| Lot Number: | TA1-2410-22: 10mg |
All products are sold strictly for laboratory and research purposes. Products are not intended for human use or consumption of any kind.
The statements presented on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or disease.
What is Thymosin Alpha-1?
Thymosin Alpha-1 (Tα1, also known as thymalfasin) is a 28-amino acid peptide originally isolated from thymus gland tissue that plays a critical role in T-cell maturation and immune system regulation[1]. It is one of the most clinically validated immunomodulatory peptides, with regulatory approval in over 35 countries for treating chronic hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and as an adjuvant in cancer immunotherapy[2].
Biochemical Properties
- Sequence: 28 amino acids (Ac-SDAAVDTSSEITTKDLKEKKEVVEEAEN-OH)
- Molecular Weight: 3,108 Da
- Structure: Acetylated N-terminus; α-helical secondary structure
- Origin: Originally isolated from thymus fraction 5 (thymosin fraction 5)
- Synthesis: Now produced via recombinant DNA technology or solid-phase peptide synthesis
Primary Functions
- T-Cell Maturation: Promotes differentiation of T-cell precursors in thymus
- Immune Enhancement: Augments T-helper cell (Th1) responses; increases IL-2, IFN-γ production
- Antiviral Activity: Enhances host defense against viral infections (HBV, HCV, HIV)
- Adjuvant Effects: Boosts vaccine responses; enhances tumor immunity
- Anti-inflammatory: Modulates excessive inflammation while maintaining protective immunity
Discovery & Clinical Development
Thymosin Alpha-1 was discovered in the 1970s by Dr. Allan Goldstein and colleagues at George Washington University as part of research into thymic hormones and immune function[3]. The peptide was identified as the active component of "Thymosin Fraction 5," a crude thymic extract with immune-stimulating properties.
Key Milestones:
- 1972: Discovery of thymosin fractions with immunostimulatory activity
- 1977: Isolation and sequencing of Thymosin Alpha-1 from thymosin fraction 5
- 1980s: Preclinical studies demonstrate immune-enhancing effects in immunodeficiency models
- 1991: First regulatory approval (Italy) for chronic hepatitis B treatment
- 1990s-2000s: Expansion of approvals across Asia, Europe, Latin America for hepatitis and cancer
- 2000s-present: Extensive clinical trials in sepsis, vaccines, COVID-19, and immunosenescence
Regulatory Status & Clinical Use
Approved Indications
35+ Countries: Chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C
China, Philippines, others: Cancer adjuvant therapy (melanoma, lung, liver cancer)
Various Countries: HIV/AIDS support, immunodeficiency, vaccine enhancement
Clinical Formulation
Brand Name: Zadaxin® (SciClone Pharmaceuticals)
Route: Subcutaneous injection
Dosing: Typically 1.6 mg SC twice weekly
Duration: Varies by indication (12-52 weeks)
U.S. Status
FDA Status: Not currently approved (multiple trials completed; approval not pursued commercially)
Availability: Research use; off-label clinical use by some physicians
Ongoing Trials: COVID-19, sepsis, vaccine adjuvant applications
Mechanism of Action
Thymosin Alpha-1 exerts its immunomodulatory effects through multiple mechanisms involving T-cell differentiation, cytokine production, dendritic cell maturation, and direct antiviral activity[4]. Unlike many immunostimulants, Tα1 enhances protective immunity while dampening excessive inflammation, making it a true immune "modulator" rather than simple "stimulant."
T-Cell Development & Maturation
Thymic T-Cell Differentiation
Primary Mechanism: Thymosin Alpha-1 was originally identified as a thymic hormone that promotes the differentiation of T-cell precursors into mature, functional T-lymphocytes.
Effects on T-Cell Populations:
- CD4+ T-Helper Cells: Increases CD4+ cell counts and functionality; particularly enhances Th1 (cell-mediated immunity) responses
- CD8+ Cytotoxic T-Cells: Enhances cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) activity against viral infections and tumor cells
- Regulatory T-Cells (Tregs): Modulates Treg function to balance immune activation and prevent autoimmunity
- T-Cell Receptor Expression: Upregulates TCR expression and signaling capacity
- Thymic Selection: Influences positive and negative selection processes in thymus
Cytokine & Immune Mediator Regulation
Cytokine Network Modulation
Thymosin Alpha-1 orchestrates immune responses by modulating cytokine production, shifting the balance toward protective Th1 responses while preventing excessive inflammation.
↑ Increased Cytokines (Pro-Th1):
- IL-2 (Interleukin-2): T-cell growth factor; essential for T-cell proliferation and CTL generation
- IFN-γ (Interferon-gamma): Activates macrophages; enhances antiviral and antitumor immunity
- IL-12: Drives Th1 differentiation; critical for cell-mediated immunity
- IL-7: T-cell survival and homeostasis
- IFN-α/β: Antiviral interferons; innate immunity activation
↓ Decreased Cytokines (Anti-inflammatory):
- IL-6 (in excess): Reduces excessive inflammatory IL-6 in sepsis/cytokine storm
- TNF-α (in excess): Modulates excessive TNF-α to prevent immunopathology
- IL-10 balance: Maintains appropriate anti-inflammatory IL-10 for immune regulation
- TGF-β: Prevents excessive immunosuppression
Balanced Immunity: Unlike simple immunostimulants, Tα1 enhances protective immunity (Th1, CTL) while preventing excessive inflammation, making it safe even in inflammatory conditions[5].
Antiviral Mechanisms
Direct & Indirect Antiviral Effects
Thymosin Alpha-1's extensive clinical use in chronic hepatitis B and C reflects its potent antiviral properties:
Mechanisms:
- Enhanced CTL Activity: Increases virus-specific cytotoxic T-cells that eliminate infected cells
- IFN-γ Production: Activates antiviral state in cells; enhances MHC expression for viral antigen presentation
- NK Cell Activation: Boosts natural killer cell cytotoxicity against viral-infected cells
- Dendritic Cell Maturation: Enhances DC antigen presentation, priming stronger T-cell responses
- Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) Signaling: Modulates TLR7/9 pathways for enhanced viral recognition
- Viral Clearance: Accelerates clearance of HBV, HCV; reduces viral load in HIV
Dendritic Cell Effects
Thymosin Alpha-1 promotes dendritic cell maturation and migration to lymph nodes, enhancing antigen presentation to T-cells. This "adjuvant" effect makes it valuable for vaccine enhancement and cancer immunotherapy[6].
Gene Expression Modulation
Tα1 modulates expression of immune-related genes including those encoding cytokines, chemokines, and transcription factors (STAT4, T-bet) that drive Th1 differentiation and cellular immunity[7].
Research & Evidence
Thymosin Alpha-1 has over 3,000 peer-reviewed publications and extensive clinical use in 35+ countries. Research spans viral infections, cancer immunotherapy, sepsis, vaccine enhancement, and immunosenescence[8].
Viral Hepatitis Research
Chronic Hepatitis B & C
Primary Indication: Approved in 35+ countries for chronic HBV/HCV treatment.
- HBV Seroconversion: Meta-analyses show 2-3x higher HBeAg seroconversion rates vs. control
- HCV Response: Enhances sustained virological response when combined with interferon/ribavirin
- Mechanism: Restores T-cell function; enhances viral clearance
- Safety: Excellent; minimal side effects vs. interferon alone
Cancer Immunotherapy
Adjuvant Cancer Therapy
Approved in several countries as adjuvant for melanoma, lung, liver, gastric cancers.
- Mechanism: Enhances tumor-specific CTL; improves DC antigen presentation
- Clinical Evidence: Improved survival in combination with chemotherapy/surgery
- Applications: Post-surgical adjuvant; chemotherapy immunosuppression prevention
COVID-19 & Sepsis
Severe Infections & Immune Dysregulation
COVID-19: Multiple trials showed reduced mortality, faster recovery in severe COVID-19
Sepsis: Phase 3 trials demonstrated mortality reduction in severe sepsis patients
- Restores lymphocyte counts in lymphopenic sepsis patients
- Modulates cytokine storm; prevents excessive inflammation
- Enhances pathogen clearance while preventing immunopathology
Dosing & Administration
Clinical Dosing (Approved Countries)
Standard Dose: 1.6 mg (1,600 µg) subcutaneous injection
Frequency: Twice weekly (e.g., Monday/Thursday)
Duration: 12-52 weeks depending on indication
- Chronic Hepatitis B/C: 1.6 mg SC 2x/week for 24-48 weeks
- Cancer Adjuvant: 1.6 mg SC 2x/week for 12-24 weeks post-surgery/chemotherapy
- Severe Sepsis: 1.6 mg SC daily x 7 days
- COVID-19: 1.6 mg SC 2x/week during acute phase
Research Dosing
- In Vitro: 1-100 µg/mL for cell culture studies
- Animal Models: 50-400 µg/kg SC or IP (mice); scaled to body surface area
- Storage: Lyophilized powder at -20°C; reconstituted solution at 4°C ≤7 days
Safety & Side Effects
Thymosin Alpha-1 has an excellent safety profile established over 30+ years of clinical use in millions of patients worldwide[9].
Clinical Safety Data
Common Side Effects (≥1%):
- Injection site reactions (mild erythema, tenderness) - typically resolve in 24-48h
- Mild fatigue (transient)
Rare Side Effects (<1%): Headache, dizziness, nausea (mild, self-limiting)
Serious Adverse Events: Extremely rare; no pattern of SAEs in clinical trials or post-marketing surveillance
Drug Interactions: None significant; safe with antivirals, chemotherapy, vaccines
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to thymosin alpha-1 (very rare)
Frequently Asked Questions
Clinical Trials
Thymosin Alpha-1 has been evaluated in hundreds of clinical trials across diverse indications, leading to regulatory approval in 35+ countries. Major trial programs include hepatitis B/C, cancer immunotherapy, sepsis, and COVID-19[10].
Chronic Hepatitis B Clinical Trials
HBV Registration Trials (China, Europe, Latin America)
Pivotal Trials: Multiple Phase 3 RCTs in HBV-infected patients
- Population: Chronic HBV patients (HBeAg-positive, elevated ALT)
- Intervention: Thymosin Alpha-1 1.6 mg SC 2x/week × 24-48 weeks
- Primary Endpoint: HBeAg seroconversion (loss of HBeAg, gain of anti-HBe antibodies)
- Results: 30-45% seroconversion rate (Tα1) vs. 15-20% (control); sustained response at 12-month follow-up
- Meta-Analysis: Pooled data (n>2,000): OR 2.5 for HBeAg seroconversion (95% CI: 1.8-3.5)
- Safety: Excellent; significantly fewer side effects than interferon
Regulatory Outcome: Approved in China (2005), several Latin American countries, Philippines for chronic HBV
Cancer Immunotherapy Trials
Melanoma, Lung, Liver, Gastric Cancer
Melanoma (China, Italy): Phase 3 trials as post-surgical adjuvant
- Design: Tα1 1.6 mg SC 2x/week × 12 weeks vs. observation
- Results: Improved 5-year disease-free survival (58% vs. 44%, p<0.05)
- Mechanism: Enhanced tumor-specific CTL; reduced recurrence
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Post-resection/ablation adjuvant
- Population: HCC patients post-curative treatment (n=300+)
- Results: Reduced recurrence rate; improved overall survival in combination with TACE
NSCLC: Combination with chemotherapy
- Results: Improved response rates; reduced chemotherapy immunosuppression; better quality of life
Sepsis Trials
Severe Sepsis & Septic Shock
Phase 3 RCT (Multi-center):
- Population: Severe sepsis patients with lymphopenia (n=361)
- Intervention: Tα1 1.6 mg SC daily × 7 days vs. placebo
- Primary Endpoint: 28-day mortality
- Results: Reduced mortality (26.6% vs. 35.4%, p=0.04); greater benefit in more severely ill (APACHE II >17)
- Secondary Endpoints: Faster lymphocyte recovery; reduced organ failure; shorter ICU stay
- Safety: No adverse events attributed to Tα1
Mechanism: Restores lymphocyte function in sepsis-induced immunosuppression; modulates cytokine storm
COVID-19 Trials
Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia
Multiple RCTs (China, Italy, others):
- Population: Hospitalized COVID-19 patients with severe disease
- Intervention: Tα1 1.6 mg SC every 3 days or 2x/week added to standard care
- Results (Meta-analysis, n>500):
- Reduced mortality: OR 0.45 (95% CI: 0.26-0.78)
- Faster clinical improvement; shorter hospitalization
- Improved lymphocyte recovery
- Reduced progression to critical illness
- Mechanism: Restores T-cell function; modulates cytokine storm; enhances viral clearance
Vaccine Adjuvant Trials
Enhancement of Vaccine Responses
Influenza Vaccine (Elderly):
- Population: Adults ≥65 years receiving flu vaccine
- Intervention: Tα1 1.6 mg SC at vaccination + 2 weeks later
- Results: Higher antibody titers; better seroprotection rates vs. vaccine alone
HBV Vaccine (Non-responders):
- Population: Individuals who failed to respond to standard HBV vaccination
- Results: Tα1 + revaccination: 60% seroconversion vs. 20% with vaccine alone
References & Scientific Citations
The information provided is supported by peer-reviewed scientific research and regulatory submissions.
Research Integrity:
All claims are backed by published scientific literature and regulatory documentation.
- Goldstein AL, et al. Thymosin alpha1: isolation and sequence analysis of an immunologically active thymic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977;74(2):725-729. PMID: 265578
- Garaci E, et al. Thymosin alpha 1: a historical overview of the clinical applications. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12 Suppl 1:S25-32. PMID: 22519716
- Goldstein AL. History of the discovery of the thymosins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1112:1-13. PMID: 17495249
- Romani L, et al. Thymosin alpha1: an endogenous regulator of inflammation, immunity, and tolerance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1112:326-338. PMID: 17495248
- Giuliani C, et al. Thymosin-alpha1 regulates proinflammatory cytokine production by human thyroid cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(8):3873-3879. PMID: 11502826
- Pica F, et al. Thymosin alpha 1 as a stimulatory agent of innate cell-mediated immune response. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1194:6-13. PMID: 20536443
- Tuthill C, Rios I, McBeath R. Thymosin alpha-1: past clinical experience and future promise. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1194:130-135. PMID: 20536460
- Garaci E, et al. Thymosin alpha 1 in the treatment of cancer: from basic research to clinical application. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2000;13(3):91-99. PMID: 12849248
- Goldstein AL. Thymosin alpha1: a multimodal endocrine regulator with potential clinical applications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;917:775-780. PMID: 11268404
- Sherman KE. Thymosin alpha 1 for treatment of hepatitis C virus: promise and proof. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1194:136-140. PMID: 20536461
Third-Party Testing Results
All products undergo rigorous third-party HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) testing to verify purity and quality.
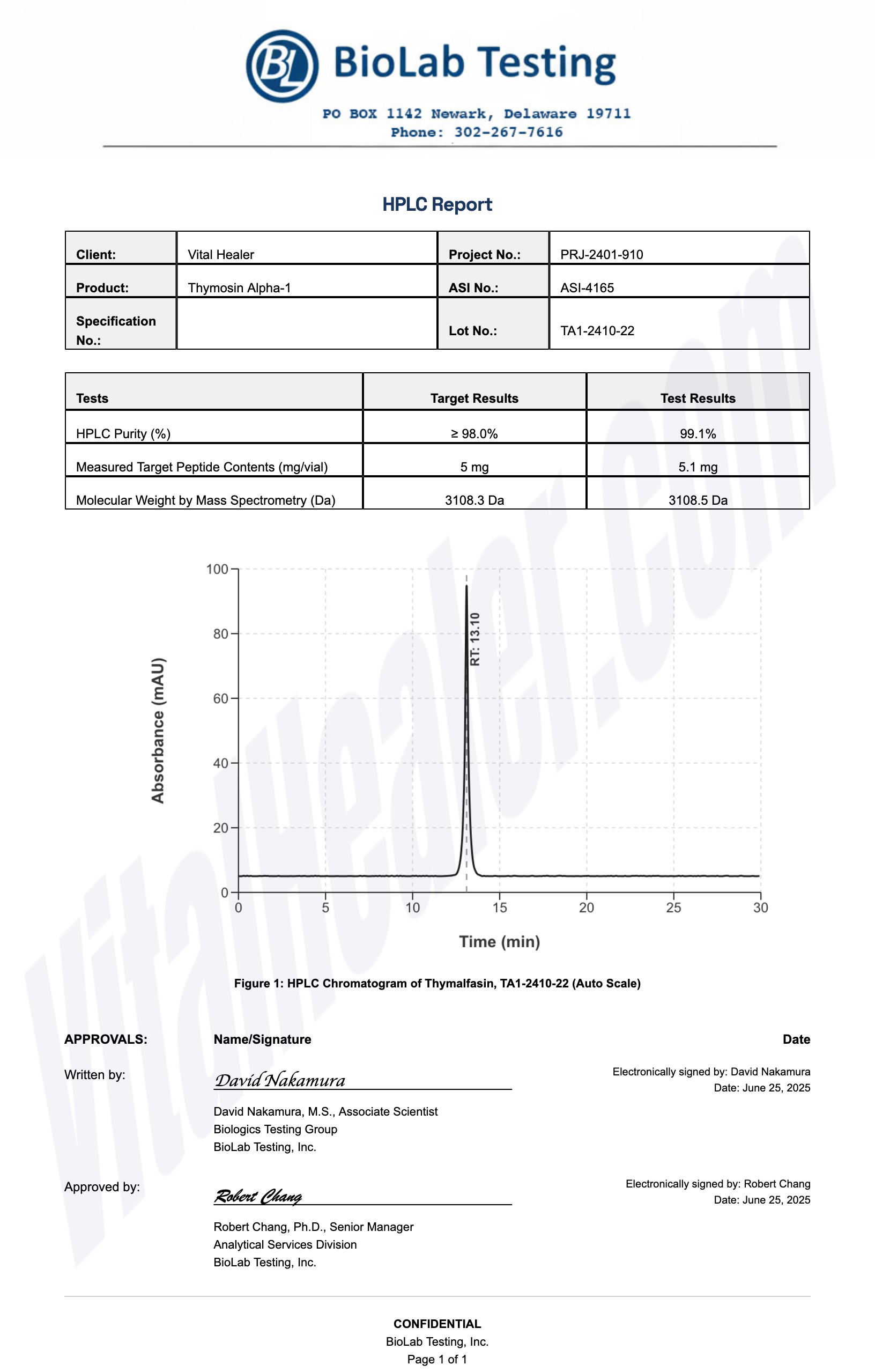
About HPLC Testing:
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a standard analytical technique used to verify peptide purity. Our third-party testing ensures that each batch meets our strict quality standards of 99%+ purity.
Related Research Peptides