BPC-157 Peptide
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound-157) is a synthetic pentadecapeptide derived from a protective protein found in human gastric juice. This 15-amino acid sequence has been extensively studied for its remarkable tissue protective and regenerative properties.
Key Research Properties:
| SKU: | VHL-BPC-001 |
|---|---|
| Purity: | 99% (HPLC Verified) |
| Form: | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C |
| CAS Number: | 137525-51-0 |
| Lot Number: | BPC-2410-01: 5mg, 10mg, 15mg |
All products are sold strictly for laboratory and research purposes. Products are not intended for human use or consumption of any kind.
The statements presented on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or disease.
What is BPC-157?
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound-157) is a synthetic pentadecapeptide derived from a protective protein found in human gastric juice. This 15-amino acid sequence has been extensively studied for its remarkable tissue protective and regenerative properties.
Originally isolated from gastric secretions, BPC-157 represents a stable fragment of the larger body protection compound naturally present in the GI tract[1]. Its designation as "BPC-157" reflects its role as the 157th compound identified in the body protection series, with significant research demonstrating its cytoprotective effects across multiple tissue types[2].
Key Research Properties
BPC-157 demonstrates unique characteristics that distinguish it from other regenerative peptides[5]:
- Exceptional Stability: Resistant to gastric acid degradation and stable at body temperature, making it highly bioavailable across multiple administration routes.
- Broad Tissue Specificity: Unlike many peptides with narrow tissue specificity, BPC-157 demonstrates beneficial effects across musculoskeletal, gastrointestinal, vascular, and neural tissues[5].
- Multi-Pathway Action: Simultaneously modulates angiogenesis, growth factors, inflammation, and cytoprotection for comprehensive tissue repair[4].
- Favorable Safety Profile: Extensive preclinical research shows minimal adverse effects with wide therapeutic window[5].
Molecular & Chemical Information
| Property | BPC-157 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C₆₂H₉₈N₁₆O₂₂ |
| Molecular Weight | 1419.53 g/mol |
| Sequence Length | 15 amino acids |
| CAS Number | 137525-51-0 |
| Sequence | Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val |
Chemical Structure Visualization
Below is the detailed chemical structure of BPC-157. This molecular diagram illustrates the complete amino acid sequence and spatial arrangement.
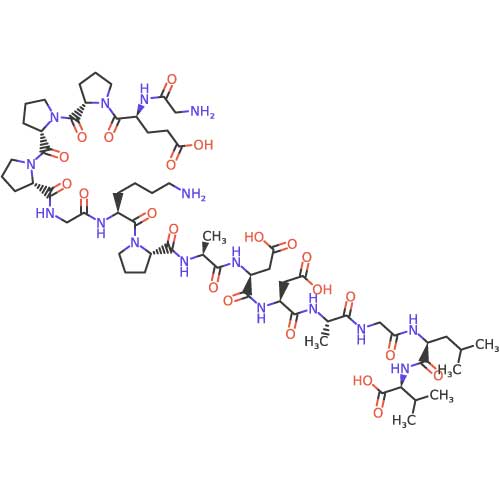
Molecular Formula: C₆₂H₉₈N₁₆O₂₂
Molecular Weight: 1419.53 g/mol
Structural Notes:
- BPC-157: A stable pentadecapeptide (15 amino acids) with a compact structure that contributes to its resistance to degradation in gastric environments[1].
- Bioavailability: The peptide's stability allows for effective delivery across multiple administration routes (subcutaneous, oral, intraperitoneal) in research models.
- Activity: The specific sequence and structure enable interaction with growth factor receptors and modulation of angiogenic pathways[3].
Key Characteristics
Gastric Origin
Derived from body protection compound (BPC) found naturally in human gastric juice. This origin contributes to its exceptional stability in acidic environments and its protective effects on GI tissues[1].
Angiogenic Properties
Promotes formation of new blood vessels through VEGF receptor modulation and endothelial cell proliferation. This angiogenic activity is central to its tissue repair capabilities[3].
Cytoprotective Effects
Protects cells from various stressors including oxidative damage, inflammation, and ischemia. Research demonstrates protective effects across multiple organ systems[4].
Broad Tissue Specificity
Unlike many peptides with narrow tissue specificity, BPC-157 demonstrates beneficial effects across musculoskeletal, gastrointestinal, vascular, and neural tissues[5].
Quality Assurance & Testing
Every batch of BPC-157 from Vital Healer Labs undergoes comprehensive third-party testing to ensure pharmaceutical-grade quality:
Purity
Verified by HPLC
Identity Confirmed
Mass Spectrometry
Party Tested
Independent Lab
- HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography): Verifies purity and concentration
- Mass Spectrometry: Confirms molecular weight and peptide identity
- Amino Acid Analysis: Validates complete sequence accuracy
- Endotoxin Testing: Ensures levels are within acceptable limits for research
- Sterility Testing: Confirms absence of microbial contamination
Mechanism of Action
BPC-157 exerts its tissue protective and regenerative effects through multiple interconnected biochemical pathways, making it one of the most versatile peptides in regenerative research.
1. Angiogenesis & Vascular Repair
One of BPC-157's most well-documented mechanisms is its pro-angiogenic activity through VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) pathway modulation[3]:
- VEGF Receptor Interaction: BPC-157 influences VEGF receptor expression and activation, promoting endothelial cell proliferation and migration
- Nitric Oxide Pathway: Enhances NO-mediated vasodilation and vascular function, contributing to improved blood flow to injured tissues[6]
- Blood Vessel Formation: Stimulates formation of new capillaries and collateral circulation, crucial for healing hypoxic tissues
Research Insight:
Studies demonstrate that BPC-157 accelerates angiogenesis in wound healing models, with significant increases in vascular density observed within 7-14 days of treatment[3].
2. Growth Factor Modulation
BPC-157 influences multiple growth factor systems critical for tissue repair[7]:
Upregulated Factors
- VEGF (vascular repair)
- EGF (epithelial growth)
- FGF (fibroblast function)
- Growth hormone receptors
Downstream Effects
- Enhanced cell proliferation
- Improved cell survival
- Accelerated differentiation
- Increased collagen synthesis
3. Fibroblast Activation & ECM Remodeling
BPC-157 significantly impacts fibroblast function and extracellular matrix production:
- Fibroblast Proliferation: Promotes fibroblast migration to injury sites and increases proliferation rates[1]
- Collagen Production: Upregulates collagen Type I and III synthesis, essential for structural tissue repair
- Matrix Metalloproteinase Balance: Helps regulate MMP activity for proper ECM remodeling without excessive degradation
- Tendon Outgrowth: Specifically enhances tendon cell outgrowth and tendon-to-bone healing[1]
4. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms
BPC-157 demonstrates potent anti-inflammatory activity through multiple pathways[8]:
| Pathway | Effect | Result |
|---|---|---|
| NF-κB Signaling | Inhibits activation | Reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines |
| Macrophage Polarization | Promotes M2 phenotype | Enhanced resolution of inflammation |
| Oxidative Stress | Reduces ROS production | Protection from oxidative damage |
| Cytokine Modulation | Balances IL-6, TNF-α | Controlled inflammatory response |
5. Cytoprotection & Cell Survival
BPC-157 protects cells from various stressors:
- Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Protects tissues from damage during restoration of blood flow
- Apoptosis Inhibition: Reduces programmed cell death in stressed tissues
- Membrane Stabilization: Helps maintain cellular membrane integrity under stress
- Mitochondrial Protection: Preserves mitochondrial function during injury
Unique Multi-System Activity:
Unlike many peptides with narrow mechanisms, BPC-157's ability to simultaneously modulate angiogenesis, growth factors, inflammation, and cytoprotection makes it exceptionally effective for comprehensive tissue repair research[5].
Research Applications
BPC-157 has been studied across numerous tissue types and injury models, demonstrating broad therapeutic potential in preclinical research.
Tendon & Ligament Healing
Extensive research demonstrates BPC-157's effects on tendon repair[1]:
- Accelerates tendon-to-bone healing in Achilles tendon models
- Promotes tendon cell outgrowth, survival, and migration
- Enhances collagen organization and fiber alignment
- Improves biomechanical strength of repaired tendons
Muscle Injury Studies
- Accelerates muscle regeneration after crush injury
- Reduces fibrosis and scar tissue formation
- Improves functional recovery metrics
- Protects against atrophy during immobilization
Bone & Joint Research
- Promotes fracture healing with improved callus formation
- Potential protective effects on cartilage in arthritis models
- Enhances integration of bone grafts
Given its gastric origin, BPC-157 has been extensively studied for GI protection[2]:
- Ulcer Healing: Accelerates healing of gastric and duodenal ulcers in various injury models
- Mucosal Protection: Prevents NSAID and alcohol-induced gastric damage
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Shows promise in colitis models with reduced inflammation
- Fistula Healing: Promotes healing of experimental GI fistulas
- Esophageal Repair: Protects against esophageal damage and promotes healing
Research demonstrates significant vascular effects[6]:
- Ischemia-Reperfusion: Protects tissues from ischemic damage and reperfusion injury
- Angiogenesis: Promotes new blood vessel formation in hypoxic tissues
- Blood Flow: Improves regional blood flow through NO pathway activation
- Thrombosis Prevention: May help prevent pathological clot formation
- Vessel Integrity: Supports endothelial function and vessel wall stability
Dermal wound studies show accelerated healing[9]:
- Faster wound closure rates in incisional and excisional models
- Enhanced re-epithelialization and granulation tissue formation
- Improved collagen deposition and organization
- Reduced scarring and improved cosmetic outcomes
- Effective in diabetic wound models with impaired healing
Emerging research on neuroprotective effects[10]:
- Peripheral Nerve Injury: Promotes nerve regeneration and functional recovery
- Traumatic Brain Injury: Neuroprotective effects in TBI models
- Spinal Cord Injury: May support recovery in SCI research models
- Neurotransmitter Systems: Influences dopaminergic and serotonergic pathways
Research Dosing Guidelines
The following information is provided for research reference only. All dosing should be determined by qualified researchers based on specific research protocols and models.
Reconstitution Instructions
- Use bacteriostatic water or sterile water for reconstitution
- Add water slowly down the side of the vial to avoid foaming
- Do not shake vigorously; allow to dissolve naturally or gently swirl
- 5mg vial: Add 1mL for 5mg/mL concentration (or 2mL for 2.5mg/mL)
- 10mg vial: Add 2mL for 5mg/mL concentration (or 4mL for 2.5mg/mL)
- Allow 2-3 minutes for complete dissolution
Storage Requirements
| State | Temperature | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Lyophilized (powder) | 2-8°C (refrigerator) or -20°C (freezer) | 3-4 months at room temp, 2+ years frozen |
| Reconstituted | 2-8°C (refrigerator) only | Up to 30 days with bacteriostatic water |
| Reconstituted (sterile water) | 2-8°C (refrigerator) only | Up to 5-7 days |
Research Dosing Considerations
Research protocols vary significantly based on study objectives, animal models, and injury types. Common parameters from published research include:
- Animal Models: 10 μg/kg to 10 mg/kg body weight (varies by species and model)
- Frequency: Once or twice daily in most protocols
- Duration: Typically 7-28 days depending on injury model
- Administration Routes: Subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, intramuscular, or oral in research
Stability Note:
BPC-157 demonstrates exceptional stability compared to many peptides. Research shows it remains active in gastric acid and at body temperature, contributing to its effectiveness across multiple administration routes[1].
Handling Best Practices
- Always use aseptic technique when reconstituting and handling
- Avoid freeze-thaw cycles with reconstituted solution
- Protect from prolonged exposure to light
- Use calibrated syringes for accurate measurement
- Document all preparation and storage conditions
All products are sold strictly for laboratory and research purposes. Products are not intended for human use or consumption of any kind.
The statements presented on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or disease.
Safety Profile & Preclinical Observations
BPC-157 has demonstrated a favorable safety profile in extensive preclinical research, with minimal adverse effects reported across numerous animal studies.
Preclinical Safety Data
- No significant toxicity at therapeutic doses in animal models
- Wide therapeutic window between effective and toxic doses
- No mutagenic or carcinogenic effects in standard assays
- Well-tolerated across various administration routes
- Minimal impact on standard hematology and biochemistry panels
- Naturally-derived sequence from human gastric juice
- Stable in acidic and neutral pH environments
- Rapid clearance prevents accumulation
- No significant drug-drug interactions reported
- Reversible effects upon discontinuation
Organ System Safety (Preclinical)
| System | Research Observations |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Generally protective effects; improved endothelial function; no arrhythmias reported |
| Gastrointestinal | Protective effects on GI mucosa; reduced ulceration; improved gut integrity |
| Hepatic | No hepatotoxicity; potential hepatoprotective effects in injury models |
| Renal | No nephrotoxicity; possible nephroprotective properties |
| Hematologic | Improved platelet function in some models; no hematologic toxicity |
| Neurological | Neuroprotective in various models; no neurotoxicity observed |
Research Contraindications & Considerations
Theoretical Contraindications in Research:
- Active malignancy: Pro-angiogenic effects raise theoretical concerns about tumor angiogenesis
- Retinopathy models: Angiogenic activity may complicate retinal pathology research
- Pregnancy/lactation studies: Insufficient safety data for reproductive research
- Pediatric models: Limited developmental safety data
Reported Observations from Research
In animal studies, the following have been occasionally noted:
- Transient injection site reactions (mild)
- Increased vascular density (expected pharmacology)
- Temporary changes in blood pressure (usually beneficial)
- Altered pain thresholds in some neuropathy models
Potential Drug Interactions (Theoretical)
While no significant interactions have been documented, theoretical considerations for research protocols include:
- Anti-coagulants: Potential additive effects on blood flow and platelet function
- Growth factors: May have synergistic effects with other angiogenic compounds
- NSAIDs: BPC-157 may counteract NSAID-induced gastric damage
- Corticosteroids: May have opposing effects on tissue repair processes
- Chemotherapy agents: Angiogenic effects may theoretically interfere with anti-angiogenic therapies
Long-Term Safety Considerations
- Most research studies have been short to medium term (days to weeks)
- Long-term safety data (months to years) is limited
- No evidence of tolerance or dependency in animal models
- Effects appear reversible upon discontinuation
- No accumulation with repeated dosing observed
Research Standards:
All research involving BPC-157 should follow appropriate institutional review board (IRB) or institutional animal care and use committee (IACUC) guidelines. Proper documentation, ethical approval, and safety monitoring protocols must be implemented according to institutional and regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Status:
BPC-157 is not approved by the FDA or any regulatory agency for human or veterinary use. It is available solely as a research chemical for in-vitro laboratory research. Claims about therapeutic benefits refer only to preclinical research findings.
Frequently Asked Questions
BPC-157 possesses several unique characteristics:
- Gastric origin: Derived from naturally occurring body protection compound in human gastric juice
- Exceptional stability: Resistant to gastric acid and stable at body temperature, unlike many peptides that require careful handling
- Broad tissue specificity: Effective across musculoskeletal, GI, vascular, and neural tissues rather than single-system activity
- Multiple mechanisms: Simultaneously affects angiogenesis, growth factors, inflammation, and cytoprotection
- Favorable safety profile: Extensive preclinical research shows minimal adverse effects[5]
Lyophilized (powder) form:
- Short-term (3-4 months): Room temperature or refrigerator (2-8°C) acceptable
- Long-term (1-2+ years): Freezer at -20°C or colder recommended
- Keep away from direct light and moisture
After reconstitution:
- Must be refrigerated at 2-8°C immediately
- With bacteriostatic water: Stable up to 30 days
- With sterile water only: Use within 5-7 days
- Do NOT freeze reconstituted solution
- Protect from prolonged light exposure
Our BPC-157 is guaranteed to be 99%+ pure, verified through comprehensive third-party testing:
- HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography): Quantifies purity percentage and confirms concentration
- Mass Spectrometry: Verifies exact molecular weight (1419.53 g/mol) and peptide identity
- Amino Acid Analysis: Validates complete 15-amino acid sequence accuracy
- Endotoxin Testing (LAL assay): Ensures endotoxin levels below 1 EU/mg
- Sterility Testing: Confirms absence of bacterial and fungal contamination
Third-party certificates of analysis (COA) are available upon request for each batch.
- Remove vial from refrigerator and allow to reach room temperature (5-10 minutes)
- Use bacteriostatic water (0.9% benzyl alcohol) for longer stability, or sterile water for short-term use
- Wipe rubber stopper with alcohol swab
- Draw appropriate volume of water into sterile syringe
- Inject water slowly down the side of the vial to avoid foaming
- Do NOT shake vigorously - gently swirl or let dissolve naturally (2-3 minutes)
- Solution should be clear and colorless when fully dissolved
- Refrigerate immediately after reconstitution
Note: Always use proper aseptic technique. Shaking can denature peptides and reduce effectiveness.
BPC-157 has been studied extensively in preclinical research across multiple areas:
- Musculoskeletal healing: Tendon, ligament, muscle, and bone repair studies showing accelerated healing and improved functional outcomes[1]
- Gastrointestinal protection: Ulcer healing, mucosal protection, inflammatory bowel disease models[2]
- Angiogenesis: Blood vessel formation, ischemia-reperfusion injury, wound healing[3]
- Neuroprotection: Peripheral nerve injury, traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury research[10]
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Various inflammatory disease models[8]
See the "References & Citations" tab for complete bibliography with links to primary literature.
NO. This product is FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY.
BPC-157 is not approved by the FDA or any regulatory agency for human consumption, medical use, or veterinary applications. It is classified as a research chemical intended solely for in-vitro laboratory research by qualified professionals. Any other use is strictly prohibited by law. All therapeutic claims refer exclusively to preclinical research findings.
BPC-157 and TB-500 are both studied for tissue repair but work through different mechanisms:
| Aspect | BPC-157 | TB-500 |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Gastric peptide | Thymosin Beta-4 fragment |
| Size | 15 amino acids | 43 amino acids |
| Primary Mechanism | Angiogenesis, growth factors | Actin regulation, cell migration |
| Tissue Specificity | Very broad (GI, MSK, vascular) | Primarily musculoskeletal |
| Stability | Exceptional (gastric acid stable) | Good (acetylated) |
Many researchers use them together for synergistic effects. See our BPC-157 & TB-500 Blend product.
Yes, we ship to most international destinations. Key points:
- Domestic (USA) orders: Typically ship within 24 hours via USPS Priority or FedEx
- International shipping: Available to most countries, 7-14 business days transit time
- Cold chain packaging: All shipments include insulation and gel packs to maintain product stability
- Buyer responsibility: Customers are responsible for compliance with local laws and import regulations
- Restricted countries: Some countries have import restrictions on research peptides - please verify legality before ordering
- Customs: Package declared as "research chemical" or "laboratory reagent" with appropriate documentation
Clinical Trials
BPC-157 has one registered clinical trial on ClinicalTrials.gov - a Phase I safety and pharmacokinetics study conducted in healthy volunteers[1].
NCT02637284 - Unknown Status
Phase I Safety & Pharmacokinetics Study
Trial Information:
- Status: Unknown (last update 2015)
- Official Title: "PCO-02 - Safety and Pharmacokinetics Trial"
- Full Title: "Phase I, pilot study in healthy volunteers, to assess the safety and pharmacokinetics of PCO-02, which active ingredient is BPC-157, a pentadecapeptide from gastric source"
- Protocol Number: BPC-1A/B-1.2
- Phase: Phase I
- Condition: Healthy Volunteers
- Location: Hospital Angeles, Tijuana, Mexico
- ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02637284
Study Design:
- Population: 42 healthy volunteers (males and females), ages 18-35
- Study Type: Randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study
- Duration: January 1, 2015 to June 30, 2015 (6 months)
- Participant Duration: 3 weeks
- Intervention: Oral administration of PCO-02 tablets (each containing 1mg BPC-157) or placebo
Phase 1a - Single Dose:
- Three cohorts of 14 subjects each
- Single oral dose of 1, 3, or 6 tablets of PCO-02 or placebo
- Randomization 6:1 (active:placebo) in each group
- 24-hour hospital admission for monitoring
- Serial blood and urine sampling for pharmacokinetics
- One week follow-up for safety assessment
- 3-tablet cohort also received second dose after a meal
Phase 1b - Multiple Dose:
- All subjects from Phase 1a continued to Phase 1b
- 3 tablets of PCO-02 or placebo, three times daily
- Duration: 14 days
- Ambulatory protocol with clinic visits at days 0, 7, and 14
- Safety and pharmacokinetics assessment at each visit
Study Goals:
- Primary: Safety of oral BPC-157 administration (adverse event monitoring)
- Secondary: Pharmacokinetics parameters (Tmax, Cmax, T½, AUC)
Note: Study status is "Unknown" on ClinicalTrials.gov. No results have been published or posted to the registry as of current review.
References & Scientific Citations
All information on this page is supported by peer-reviewed scientific research. Below is a comprehensive bibliography of studies referenced.
Research Integrity:
We are committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information backed by published scientific literature. All claims about BPC-157's properties refer exclusively to preclinical research findings.
Primary Literature Citations
- Seiwerth S, Brcic L, Batelja Vuletic L, et al. BPC 157 and blood vessels. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2014;20(7):1121-1125. [Ingenta Connect] - Cited by 100
- Vukojević J, Milavić M, Perović D, Ilić S, et al. Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and the central nervous system. Neural Regeneration Research. 2022;17(3):482-487. [LWW] - Cited by 49
- Seiwerth S, Sikiric P, Grabarevic Z, Zoricic I, et al. BPC 157's effect on healing. Journal of Physiology-Paris. 1997;91(3-5):191-195. [ScienceDirect] - Cited by 113
- Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R, et al. Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157-NO-system relation. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2014;20(7):1126-1135. [Ingenta Connect] - Cited by 155
- Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R, et al. Brain-gut axis and pentadecapeptide BPC 157: Theoretical and practical implications. Current Neuropharmacology. 2016;14(8):857-865. [Ingenta Connect] - Cited by 91
- Chang CH, Tsai WC, Hsu YH, Su Pang JH. Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 enhances the growth hormone receptor expression in tendon fibroblasts. Molecules. 2014;19(11):19066-19077. [MDPI] - Cited by 172
- Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R, et al. Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157: novel therapy in gastrointestinal tract. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2011;17(16):1612-1632. [Bentham Direct] - Cited by 141
- Deek SA. BPC 157 as potential treatment for COVID-19. Medical Hypotheses. 2022;158:110738. [ScienceDirect] - Cited by 15
- Cerovecki T, Bojanic I, Brcic L, Radic B, et al. Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 (PL 14736) improves ligament healing in the rat. Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 2010;28(9):1155-1161. [Wiley Online Library] - Cited by 95
- Seiwerth S, Milavic M, Vukojevic J, Gojkovic S, et al. Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and wound healing. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2021;12:627533. [Frontiers] - Cited by 66
- Jóźwiak M, Bauer M, Kamysz W, Kleczkowska P. Multifunctionality and Possible Medical Application of the BPC 157 Peptide—Literature and Patent Review. Pharmaceuticals. 2025;18(2):185. [MDPI] - Cited by 10
- Vasireddi N, Hahamyan H, Salata MJ, et al. Emerging Use of BPC-157 in Orthopaedic Sports Medicine: A Systematic Review. HSS Journal. 2025;21(1):11-20. [SAGE Journals] - Cited by 2
- Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Mise S, Staresinic M, Bedekovic V, et al. Corticosteroid-impairment of healing and gastric pentadecapeptide BPC-157 creams in burned mice. Burns. 2003;29(4):323-334. [ScienceDirect] - Cited by 119
- Seiwerth S, Rucman R, Turkovic B, et al. BPC 157 and standard angiogenic growth factors. Gastrointestinal tract healing, lessons from tendon, ligament, muscle and bone healing. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2018;24(18):1972-1989. [Bentham Direct] - Cited by 105
- Cesarec V, Becejac T, Misic M, Djakovic Z, et al. Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and the esophagocutaneous fistula healing therapy. European Journal of Pharmacology. 2013;701(1-3):203-212. [ScienceDirect] - Cited by 107
- Tudor M, Jandric I, Marovic A, Gjurasin M, Perovic D, et al. Traumatic brain injury in mice and pentadecapeptide BPC 157 effect. Regulatory Peptides. 2010;160(1-3):26-32. [ScienceDirect] - Cited by 86
- Balenovic D, Bencic ML, Udovicic M, Simonji K, et al. Inhibition of methyldigoxin-induced arrhythmias by pentadecapeptide BPC 157: a relation with NO-system. Regulatory Peptides. 2009;156(1-3):83-89. [ScienceDirect] - Cited by 125
- Staresinic M, Petrovic I, Novinscak T, et al. Effective therapy of transected quadriceps muscle in rat: Gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 2006;24(5):1109-1117. [Wiley Online Library] - Cited by 131
- Mikus D, Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Petricevic A, Aralica G, et al. Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 cream improves burn-wound healing and attenuates burn-gastric lesions in mice. Burns. 2001;27(8):817-827. [ScienceDirect] - Cited by 135
- Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Brcic L, Sever M, et al. Revised Robert's cytoprotection and adaptive cytoprotection and stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Possible significance and implications for novel mediator. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2010;16(10):1224-1234. [Bentham Direct] - Cited by 136
Disclaimer:
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. The products offered are for in-vitro laboratory research use only. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat, or cure any medical condition, ailment, or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law. All research cited refers to preclinical studies only.
Additional Resources
- PubMed - Search "BPC-157" for complete research database
- Google Scholar - Academic search for BPC-157 research
- PubMed Central - Free full-text articles
- ClinicalTrials.gov - Registry of clinical research (note: limited BPC-157 trials)
Third-Party Testing Results
All products undergo rigorous third-party HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) testing to verify purity and quality.
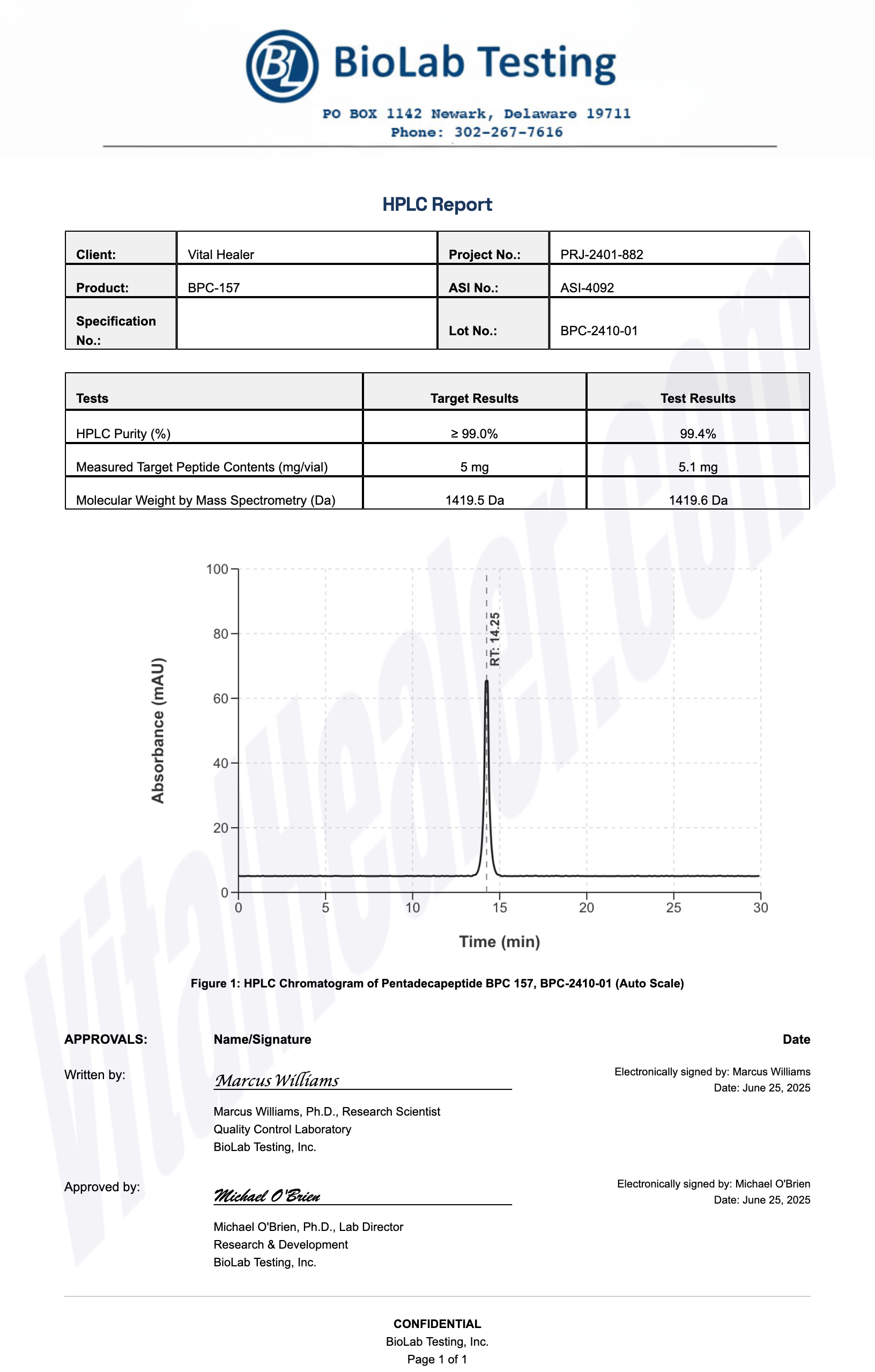
About HPLC Testing:
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a standard analytical technique used to verify peptide purity. Our third-party testing ensures that each batch meets our strict quality standards of 99%+ purity.
Related Research Peptides