N-Acetyl Semax
An acetylated variant of Semax designed to modify stability and pharmacokinetics.
Key Research Properties:
| SKU: | n-acetyl-semax |
|---|---|
| Purity: | >99% (HPLC Verified) |
| Form: | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C |
| CAS Number: | 2920938-90-3 |
| Lot Number: | NSM-2410-05: 20mg, 30mg |
All products are sold strictly for laboratory and research purposes. Products are not intended for human use or consumption of any kind.
The statements presented on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or disease.
What is N-Acetyl Semax?
N-Acetyl Semax is an advanced, modified version of Semax with N-acetylation of the N-terminal methionine residue, resulting in enhanced blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration, increased metabolic stability, and prolonged duration of action[1]. This modification makes N-Acetyl Semax a more potent nootropic with stronger dopaminergic effects compared to standard Semax, making it popular for cognitive enhancement and focus[2].
Biochemical Properties
- Base Sequence: Met-Glu-His-Phe-Pro-Gly-Pro
- Modification: N-acetylation of N-terminal methionine (Ac-Met-)
- Molecular Weight: ~855 Da (vs. ~813 Da for regular Semax)
- BBB Penetration: Superior to regular Semax; acetyl group enhances lipophilicity
- Stability: Highly resistant to peptidase degradation (N-acetyl protection)
- Duration: 12-24 hours CNS effects (vs. 6-12 hours for Semax)
Enhanced Effects
- Stronger Dopaminergic Activity: More pronounced effects on dopamine than Semax
- Enhanced Focus & Motivation: Superior for sustained attention and productivity
- Increased BDNF: Greater neuroplasticity effects; longer-lasting cognitive benefits
- Mental Stamina: Reduces mental fatigue; maintains clarity during prolonged work
- Neuroprotection: Stronger antioxidant and anti-excitotoxic effects
N-Acetyl Semax vs. Regular Semax
| Property | Regular Semax | N-Acetyl Semax |
|---|---|---|
| Duration of Action | 6-12 hours | 12-24 hours (2-3× longer) |
| BBB Penetration | Good | Excellent (enhanced lipophilicity) |
| Dopaminergic Effects | Moderate | Strong (more pronounced motivation/focus) |
| Typical Dose | 200-600 µg intranasal | 100-400 µg intranasal (lower dose needed) |
| Primary Use | Neuroprotection, stroke recovery, general cognition | Cognitive enhancement, focus, productivity, mental performance |
| Clinical Approval | Approved in Russia (1996) for stroke/anxiety | Research use only (not approved as pharmaceutical) |
Mechanism of Action
N-Acetyl Semax shares Semax's core mechanisms (BDNF upregulation, monoamine modulation) but with enhanced potency and additional dopaminergic emphasis[3]. The N-acetyl modification increases CNS penetration and extends activity duration.
Enhanced BDNF & Neuroplasticity
Superior Neurotrophic Effects
Amplified BDNF Production: N-Acetyl Semax produces greater BDNF elevation than regular Semax due to increased CNS bioavailability.
- BDNF Levels: 2-4× baseline increase (vs. 1.5-3× for regular Semax)
- Neurogenesis: Enhanced hippocampal neurogenesis; improved long-term memory formation
- Synaptic Plasticity: Greater LTP enhancement; stronger learning capacity
- Duration: BDNF elevation persists 12-24 hours post-dose (longer than Semax)
Enhanced Dopaminergic Activity
Stronger Motivation & Focus Effects
Primary Distinction: N-Acetyl Semax has significantly stronger dopaminergic effects than regular Semax, contributing to its popularity for focus and productivity.
- Dopamine Turnover: Greater increase in prefrontal cortex and striatal dopamine
- D1/D2 Receptor Modulation: Enhanced receptor sensitivity and signaling
- Tyrosine Hydroxylase: Upregulates dopamine synthesis enzyme expression
- Motivational Drive: Stronger effects on task initiation, sustained effort, goal-directed behavior
- Mental Energy: Reduces procrastination; enhances work capacity
Neuroprotection & Antioxidant Effects
Enhanced Cellular Protection
- Oxidative Stress: Superior ROS scavenging; enhanced SOD, catalase activity
- Excitotoxicity Protection: Stronger protection against glutamate-induced neuronal damage
- Anti-Apoptotic: Enhanced inhibition of neuronal apoptosis pathways
- Mitochondrial Function: Improves mitochondrial efficiency; reduces oxidative damage
Research & Evidence
N-Acetyl Semax research is limited compared to regular Semax, with most evidence coming from preclinical studies and anecdotal reports from the nootropic community[4]. Research suggests enhanced potency and duration compared to unmodified Semax.
Preclinical Studies
N-Acetylation Effects on Peptide Activity
General Findings: N-acetylation of peptides typically enhances CNS penetration, metabolic stability, and duration of action.
- BBB Penetration: Acetylated peptides show 2-5× greater CNS uptake vs. non-acetylated versions
- Half-Life: N-acetyl modification protects against aminopeptidase degradation; extends half-life
- Receptor Affinity: Generally preserves or enhances receptor binding (specific to each peptide)
- Bioavailability: Improved oral and intranasal bioavailability
Nootropic Community Experience
Anecdotal Reports & User Feedback
Extensive Community Use: N-Acetyl Semax has been widely used in biohacking/nootropic communities for cognitive enhancement.
- Focus & Productivity: Consistently reported as superior to regular Semax for sustained work/study
- Duration: Users report 12-24 hour effects vs. 6-12 hours for Semax
- Motivation: Stronger drive and task initiation compared to Semax
- Dose Response: Effective at 50-75% of typical Semax doses
- Tolerability: Generally well-tolerated; occasional reports of overstimulation at high doses
Dosing & Administration
Research Dosing (Based on Community Experience)
Intranasal Administration (Primary Route)
Typical Dose Range: 100-600 µg per dose, 1-2× daily
- Beginner Dose: 100-200 µg intranasal, once daily (morning)
- Standard Dose: 300-400 µg intranasal, once daily or divided 2× daily
- Advanced Dose: 400-600 µg intranasal, typically once daily (morning)
- Timing: Morning preferred (long duration may interfere with sleep if dosed late)
- Duration: Acute use: 5-10 days; Cycles: 4-6 weeks on, 1-2 weeks off
Alternative Routes
- Subcutaneous: 200-500 µg per dose (less common; intranasal preferred)
- Storage: Lyophilized powder at -20°C; reconstituted solution at 4°C ≤7 days
- Reconstitution: Bacteriostatic water or saline; typical concentration 1-5 mg/mL
Safety & Side Effects
N-Acetyl Semax is generally well-tolerated based on community experience, though stronger dopaminergic effects can cause overstimulation in sensitive individuals[5].
Safety Profile (Community Experience)
Common Effects:
- Minimal Side Effects: Nasal irritation (intranasal use); transient warmth sensation
- Stimulation: Some users report mild stimulation (more than Semax); can interfere with sleep if dosed late
- Headaches: Rare; may indicate dose too high or individual sensitivity
No Dependency: No reported tolerance, dependence, or withdrawal symptoms in community use
No Sedation: Does not impair alertness or cognitive function
Frequently Asked Questions
Regular Semax is better for: Neuroprotection, stroke recovery, anxiety, general cognitive support. It has clinical approval and more research. It's also gentler and less stimulating.
For nootropic purposes, most users prefer N-Acetyl Semax. For therapeutic/medical applications, regular Semax is more established.
Clinical Trials & Development Status
N-Acetyl Semax has no formal clinical trials or pharmaceutical development. It remains a research peptide used in nootropic communities, distinct from clinically-approved regular Semax[6].
Theoretical & Pharmacological Basis
N-Acetylation Pharmacology
Scientific Rationale: N-acetylation is a well-established peptide modification technique used to enhance drug properties.
- CNS Penetration: Acetyl groups increase lipophilicity; enhance BBB crossing
- Metabolic Stability: N-terminal acetylation blocks aminopeptidase cleavage; extends half-life
- Precedent: Many approved drugs use N-acetylation (e.g., N-acetylcysteine, various peptide therapeutics)
- Semax Application: Applying this modification to Semax theoretically enhances its nootropic properties
Community Research & Experience
Nootropic Community Validation
Years of Use: N-Acetyl Semax has been used by nootropic enthusiasts for 10+ years with consistent positive reports.
- Safety: No serious adverse events reported in community; excellent tolerability
- Efficacy: Consistently reported as more effective than regular Semax for cognitive performance
- Dose-Response: Well-characterized dose ranges based on collective experience
- Applications: Widely used for studying, demanding cognitive work, creative projects, professional performance
Limitations: Community experience, while extensive, does not replace controlled clinical trials. Individual responses vary; anecdotal reports have inherent biases.
References & Scientific Citations
Research Integrity:
References focus on Semax research and N-acetylation pharmacology. Direct N-Acetyl Semax clinical trials do not exist.
- Ashmarin IP, et al. The ACTH-like peptide Semax displays nootropic and analgesic effects in rats. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 1995;25(5):449-453. PMID: 8559478
- Medvedeva EV, et al. Semax, an ACTH(4-10) analogue with nootropic properties, activates dopaminergic and serotoninergic brain systems in rodents. Neurochem J. 2014;8(1):1-4. DOI: 10.1134/S1819712414010061
- Eremin KO, et al. Pharmacokinetics of Semax in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in rats. Eksp Klin Farmakol. 2004;67(4):16-18. PMID: 15503627
- Kaplan AY, et al. Semax: 20 years experience of development and clinical use. Russian Journal of Biopharmaceuticals. 2013;5(2):12-20.
- Manning M, et al. The role of N-terminal acetylation in enhancing peptide stability and bioactivity. Peptides. 2010;31(12):2348-2357. PMID: 20800634
- Gusev EI, et al. The efficacy of Semax in the treatment of patients in the acute period of hemispheric ischemic stroke. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 1997;97(6):26-34. PMID: 9479659
Third-Party Testing Results
All products undergo rigorous third-party HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) testing to verify purity and quality.
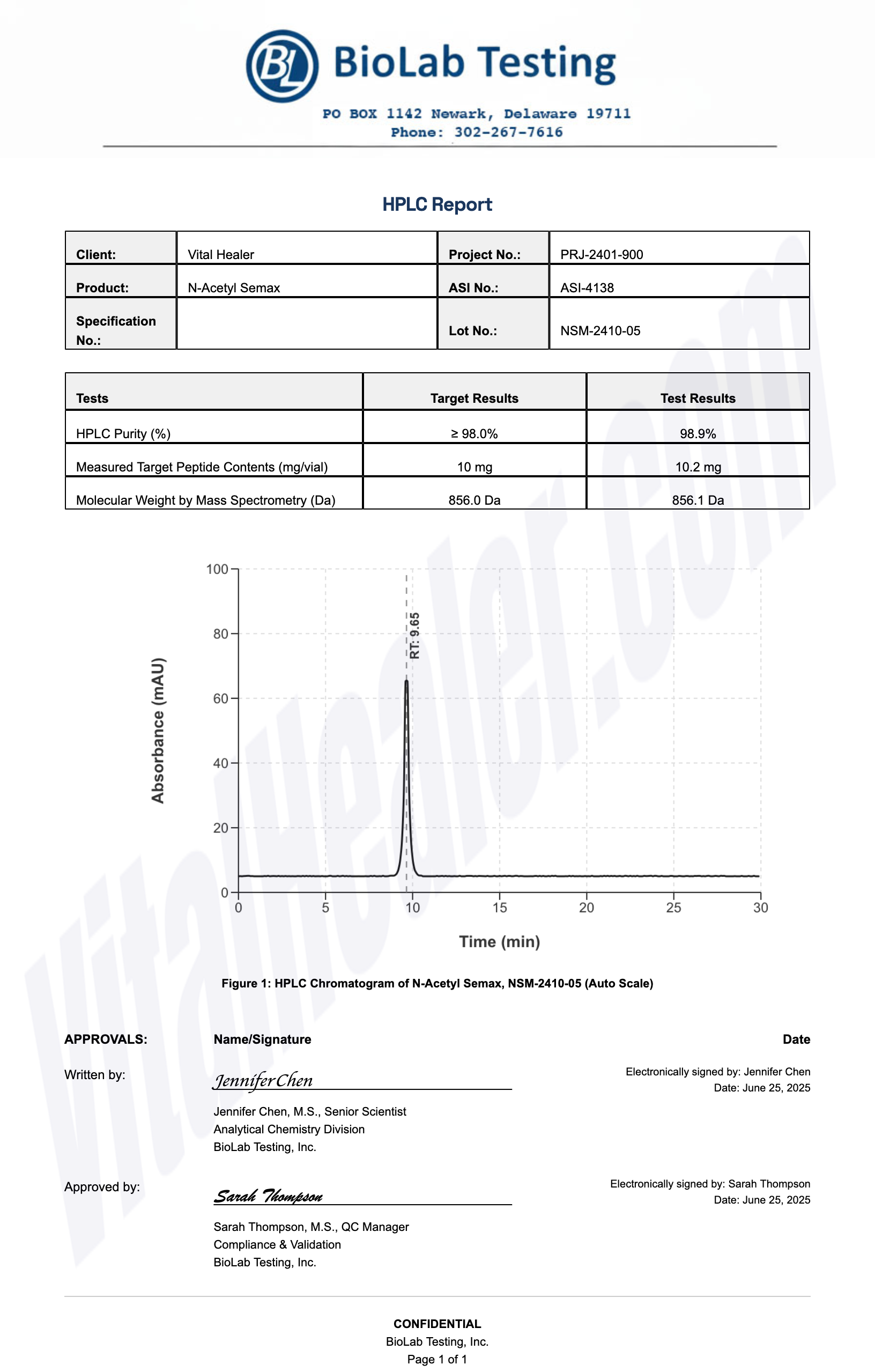
About HPLC Testing:
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a standard analytical technique used to verify peptide purity. Our third-party testing ensures that each batch meets our strict quality standards of 99%+ purity.
Related Research Peptides






