Cibinetide ARA 290
Also called cibinetide; an EPO‑derived small peptide that selectively targets the innate repair receptor.
Key Research Properties:
| SKU: | cibinetide-ara-290 |
|---|---|
| Purity: | >99% (HPLC Verified) |
| Form: | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C |
| CAS Number: | 1208243-50-8 |
All products are sold strictly for laboratory and research purposes. Products are not intended for human use or consumption of any kind.
The statements presented on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or disease.
What is Cibinetide (ARA 290)?
Cibinetide, also known as ARA 290, is a synthetic 11-amino acid peptide derived from erythropoietin (EPO) that selectively activates the innate repair receptor (IRR) without affecting erythropoiesis[1]. This EPO-derived peptide provides tissue protection, neuroprotection, and anti-inflammatory effects, particularly for neuropathic pain and metabolic neuropathy, without the hematological side effects of full EPO[2].
Biochemical Properties
- Sequence: Derived from EPO helix B region (positions 99-109)
- Structure: 11-amino acid cyclic peptide (pGlu-Glu-Met-Gln-Lys-Glu-Thr-Ala-Ala-Ala-Lys)
- Molecular Weight: ~1,229 Da
- Target: Innate repair receptor (IRR) / β-common receptor (βCR) complex
- Non-Erythropoietic: No effect on red blood cell production
- Development: Originally developed by Araim Pharmaceuticals
Key Benefits
- Neuropathic Pain Relief: Reduces diabetic and chemotherapy-induced neuropathy
- Nerve Protection: Promotes neuronal survival and repair
- Anti-Inflammatory: Reduces inflammatory cytokines and tissue inflammation
- Tissue Repair: Activates innate repair mechanisms in multiple tissues
- Metabolic Support: Improves metabolic function in neuropathy
- Safe Profile: No erythropoietic effects; excellent tolerability
Primary Research Applications
Diabetic Neuropathy
Clinical trials show significant reduction in neuropathic pain symptoms, improved nerve conduction, and better quality of life in diabetic peripheral neuropathy patients.
Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathy
Protects against paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy; reduces pain and sensory symptoms in cancer patients receiving neurotoxic chemotherapy.
Neuroprotection
Protects neurons from oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis; potential applications in neurodegenerative diseases and stroke.
Mechanism of Action
Cibinetide activates the innate repair receptor (IRR), a heteromeric complex of the β-common receptor (βCR/CD131) and tissue protection receptor (TPR), triggering anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, and tissue-protective signaling[3].
Innate Repair Receptor Activation
Selective Receptor Targeting
Receptor Specificity: Unlike full-length EPO (which binds EPO receptor for erythropoiesis AND innate repair receptor for tissue protection), Cibinetide selectively binds only the innate repair receptor.
- βCR/CD131 Complex: Binds β-common receptor (shared with GM-CSF, IL-3, IL-5)
- Tissue Protection Receptor: Forms heteromeric complex with TPR
- No EPO Receptor Binding: Does not activate classical EPO receptor (EPOR); no erythropoiesis
- Downstream Signaling: Activates JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/Akt, and ERK pathways
- Tissue Distribution: IRR expressed in neurons, endothelium, kidney, heart, and other tissues
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Cytokine Modulation & Inflammation Resolution
- TNF-α Reduction: Decreases pro-inflammatory TNF-α levels
- IL-6 Modulation: Normalizes inflammatory IL-6 signaling
- NF-κB Inhibition: Suppresses NF-κB inflammatory pathway activation
- Macrophage Polarization: Shifts macrophages from M1 (pro-inflammatory) to M2 (anti-inflammatory)
- Neutrophil Regulation: Reduces excessive neutrophil infiltration and tissue damage
Neuroprotection & Nerve Repair
Neuronal Protection & Regeneration
- Anti-Apoptotic: Activates Akt survival pathway; prevents neuronal apoptosis
- Oxidative Stress Protection: Reduces ROS; enhances antioxidant defenses
- Nerve Growth Factors: Upregulates NGF, BDNF, and other neurotrophic factors
- Axonal Regeneration: Promotes axonal growth and nerve fiber regeneration
- Myelin Protection: Protects Schwann cells and myelin integrity
- Mitochondrial Function: Improves mitochondrial function in damaged neurons
Tissue Protection & Repair
Multi-Tissue Protective Effects
- Endothelial Protection: Protects vascular endothelium; improves microvascular function
- Kidney Protection: Reduces diabetic nephropathy progression
- Cardiac Protection: Cardioprotective effects against ischemia-reperfusion injury
- Wound Healing: Accelerates tissue repair and wound closure
Research & Evidence
Cibinetide has been extensively studied in preclinical models and clinical trials, particularly for diabetic neuropathy and chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy[4].
Preclinical Evidence
Animal Model Studies
Diabetic Neuropathy Models:
- Reverses established diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rodents
- Improves nerve conduction velocity and sensory function
- Reduces pain hypersensitivity (mechanical and thermal)
- Promotes nerve fiber regeneration
Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathy:
- Protects against paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy
- Prevents cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity
- Does not interfere with chemotherapy anti-cancer effects
Other Models:
- Neuroprotection in stroke and traumatic brain injury models
- Kidney protection in diabetic nephropathy
- Cardiac protection in myocardial infarction
Clinical Studies
Human Clinical Trials
Phase II Diabetic Neuropathy Trial (2011):
- Population: 67 patients with diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy
- Results: Significant improvement in neuropathic symptoms (pain, burning, tingling)
- Safety: Well-tolerated; no erythropoietic effects; no serious adverse events
- Duration: 28-day treatment period with sustained benefits
Additional Clinical Data:
- Phase I studies demonstrated excellent safety and no effect on hemoglobin/hematocrit
- Proof-of-concept studies in sarcoidosis-associated neuropathy
- Investigation in chronic kidney disease patients
Dosing & Administration
Clinical Trial Dosing
Subcutaneous Administration
Phase II Trial Protocol (Diabetic Neuropathy):
- Dose: 4 mg subcutaneous injection
- Frequency: Once daily
- Duration: 28 days (4 weeks)
- Route: Subcutaneous injection (abdomen or thigh)
- Timing: Consistent daily timing (morning or evening)
Research Dosing Parameters
- Typical Research Dose: 2-8 mg per dose, subcutaneous
- Frequency: Once daily to every other day
- Duration: 2-4 weeks for acute protocols; up to 3 months for chronic conditions
- Storage: Lyophilized powder at 2-8°C; reconstituted solution use immediately or store at 4°C ≤7 days
- Reconstitution: Bacteriostatic water or saline; typical concentration 2-4 mg/mL
Safety & Side Effects
Cibinetide demonstrated excellent safety and tolerability in clinical trials, with no erythropoietic effects and minimal adverse events[5].
Excellent Safety Profile (Clinical Trials)
Phase II Trial Safety Data:
- No Erythropoietic Effects: No changes in hemoglobin, hematocrit, or red blood cell count
- No Serious Adverse Events: No treatment-related serious AEs reported
- Mild Side Effects: Injection site reactions (mild, transient); occasional headache
- No Cardiovascular Effects: No changes in blood pressure, heart rate, or thrombotic events
- No Immunogenicity: No antibody formation against Cibinetide detected
Dropout Rate: Very low dropout rate due to adverse events (<5% in Phase II trial)
Frequently Asked Questions
Full-Length EPO: Binds both EPO receptor (erythropoiesis) AND innate repair receptor (tissue protection); increases red blood cells; risk of polycythemia, thrombosis, hypertension.
Cibinetide isolates EPO's beneficial tissue-protective effects while eliminating hematological side effects.
Other applications: Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, sarcoidosis-associated neuropathy, chronic kidney disease, neurodegenerative diseases, stroke, and general neuroprotection.
Most clinical evidence supports its use for neuropathic pain conditions.
Clinical Trials
Cibinetide (ARA 290) has been evaluated in multiple clinical trials registered on ClinicalTrials.gov, focusing primarily on neuropathic pain and nerve fiber regeneration[1].
NCT02039687 - Completed with Results
Sarcoidosis Neuropathy: Corneal Nerve Fiber Study
Trial Information:
- Status: Completed with Results Available
- Official Title: "Study of Efficacy of ARA 290 on Corneal Nerve Fiber Density and Neuropathic Symptoms of Subjects With Sarcoidosis"
- Condition: Neuropathy of Sarcoidosis
- Locations: Cleveland, Ohio, United States; Leiden, Netherlands
- ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02039687 | View Results
Key Findings:
- ARA 290 improved corneal nerve fiber abundance in patients with sarcoidosis-associated small nerve fiber loss[7]
- Significant reduction in neuropathic pain symptoms
- Evidence of nerve fiber regeneration documented by corneal confocal microscopy
- Well-tolerated with excellent safety profile
NCT06626971 - Terminated
Diabetic Macular Edema Study
Trial Information:
- Status: Terminated
- Official Title: "The Use of ARA290 for the Treatment of Diabetic Macular Oedema"
- Condition: Diabetic Macular Oedema
- Location: Belfast, Co Antrim, United Kingdom
- ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT06626971 | View Study Details
- Related Publication: J Clin Med. 2020;9(7):2225[13]
Study Insights:
- Phase 2 trial evaluating cibinetide for diabetic macular edema treatment
- Although terminated, published results suggested potential visual improvement benefits
- Cibinetide may lead to retinal function benefits in early disease stages
NCT01933529 - Unknown Status
Type 2 Diabetes & Prediabetes Study
Trial Information:
- Status: Unknown (not updated)
- Official Title: "ARA290 in T2D (Effects of ARA 290, an Erythropoietin Analogue) in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes"
- Conditions: Diabetes Type 2, Impaired Fasting Glucose, Impaired Glucose Tolerance
- Location: Stockholm, Sweden
- ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01933529 | View Study Details
Background:
- Designed to evaluate metabolic effects of ARA 290 in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes
- Related to published findings showing improved metabolic control and neuropathic symptoms[2]
- Status unknown; may have been completed without registry update
Published Clinical Research (Not Trial Registry)
Additional Peer-Reviewed Clinical Studies
Safety & Efficacy in Sarcoidosis Neuropathy (2012):
- Randomized, double-blind pilot study in sarcoidosis patients with small fiber neuropathy
- Significant improvement in neuropathic symptoms with ARA 290 treatment
- Excellent safety profile; no serious adverse events
- Citation: Heij L, et al. Mol Med. 2012. [Cited by 122][1]
Type 2 Diabetes Metabolic & Neuropathy Study (2014):
- ARA 290 improved metabolic control in type 2 diabetes patients
- Significant reduction in neuropathic symptoms (SFNSL score decrease)
- 28-day subcutaneous daily administration protocol
- Citation: Brines M, et al. Mol Med. 2014. [Cited by 165][2]
Long-Term Neuropathic Pain Relief (2014):
- ARA 290 produced long-term relief of neuropathic pain
- Coupled with suppression of spinal microglia activation
- Disease-modulatory effects suggesting mechanism beyond symptom masking
- Citation: Swartjes M, et al. Mol Pain. 2014. [Cited by 40][3]
References & Scientific Citations
Research Integrity:
All references are from peer-reviewed journals with citation counts from Google Scholar. Studies span clinical trials, neuroprotection, tissue repair, and inflammatory modulation.
- Heij L, Niesters M, Swartjes M, Hoitsma E, Drent M, et al. Safety and efficacy of ARA 290 in sarcoidosis patients with symptoms of small fiber neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind pilot study. Molecular Medicine. 2012;18:1430-1436. [Springer] - Cited by 122
- Brines M, Dunne AN, van Velzen M, Proto PL, et al. ARA 290, a nonerythropoietic peptide engineered from erythropoietin, improves metabolic control and neuropathic symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes. Molecular Medicine. 2014;20:658-666. [Springer] - Cited by 165
- Swartjes M, van Velzen M, Niesters M, Aarts L, et al. ARA 290, a peptide derived from the tertiary structure of erythropoietin, produces long-term relief of neuropathic pain coupled with suppression of the spinal microglia response. Molecular Pain. 2014;10:13. [SAGE Journals] - Cited by 40
- Watanabe M, Lundgren T, Saito Y, Cerami A, et al. A nonhematopoietic erythropoietin analogue, ARA 290, inhibits macrophage activation and prevents damage to transplanted islets. Transplantation. 2016;100(3):564-572. [LWW] - Cited by 34
- van Velzen M, Heij L, Niesters M, Cerami A, Brines M, Dahan A. ARA 290 for treatment of small fiber neuropathy in sarcoidosis. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 2014;23(4):541-550. [Taylor & Francis] - Cited by 46
- Dahan A, Dunne A, Swartjes M, Proto PL, Heij L, et al. ARA 290 improves symptoms in patients with sarcoidosis-associated small nerve fiber loss and increases corneal nerve fiber density. Molecular Medicine. 2013;19:334-345. [Springer] - Cited by 107
- Culver DA, Dahan A, Bajorunas D, et al. Cibinetide improves corneal nerve fiber abundance in patients with sarcoidosis-associated small nerve fiber loss and neuropathic pain. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2017;58(6):BIO52-BIO60. [ARVO Journals] - Cited by 103
- Al-Onaizi MA, Thériault P, Lecordier S, et al. Early monocyte modulation by the non-erythropoietic peptide ARA 290 decelerates AD-like pathology progression. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 2022;100:62-77. [ScienceDirect] - Cited by 18
- Zhang W, Yu G, Zhang M. ARA 290 relieves pathophysiological pain by targeting TRPV1 channel: Integration between immune system and nociception. Peptides. 2016;78:79-87. [ScienceDirect] - Cited by 17
- Niesters M, Swartjes M, Heij L, Brines M, Dahan A. The erythropoietin analog ARA 290 for treatment of sarcoidosis-induced chronic neuropathic pain. Expert Opinion on Orphan Drugs. 2013;1(1):77-87. [Taylor & Francis] - Cited by 33
- Watanabe M, Saito Y, Wallmo J, et al. An engineered innate repair receptor agonist, ARA 290, protects rat islets from cytokine-induced apoptosis. Journal of Diabetes & Metabolism. 2016;7(8):708. [PDF] - Cited by 2
- Nairz M, Haschka D, Dichtl S, Sonnweber T, Schroll A, et al. Cibinetide dampens innate immune cell functions thus ameliorating the course of experimental colitis. Scientific Reports. 2017;7:13809. [Nature] - Cited by 19
- Lois N, Gardner E, McFarland M, Armstrong D, et al. A phase 2 clinical trial on the use of cibinetide for the treatment of diabetic macular edema. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020;9(7):2225. [MDPI] - Cited by 15
- Yao M, Domogatskaya A, Ågren N, et al. Cibinetide protects isolated human islets in a stressful environment and improves engraftment in the perspective of intra portal islet transplantation. Cell Transplantation. 2021;30:09636897211039739. [SAGE Journals] - Cited by 13
- Bitto A, Irrera N, Pizzino G, Pallio G, Mannino F, et al. Activation of the EPOR-β common receptor complex by cibinetide ameliorates impaired wound healing in mice with genetic diabetes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 2018;1864(2):632-642. [ScienceDirect] - Cited by 20
- Canning P, O'Leary O, Allen LD, et al. ARA290 (cibinetide) treatment confers neuroprotective effects in diabetic retinopathy, through modulation of inflammatory mediators. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2019;60(9):5136. [ARVO Journals] - Cited by 3
- Wang Y, Guan X, Tang Y, Wang M. Cibinetide Alleviate The Progression Of Apical Periodontitis Via Sirt1 Axis. International Dental Journal. 2025;75(1):S54-S55. [ScienceDirect]
- Yao M, Watanabe M, Sun S, Tokodai K, Cerami A, et al. Improvement of islet allograft function using cibinetide, an innate repair receptor ligand. Transplantation. 2020;104(10):2072-2080. [LWW] - Cited by 7
- Monis A, Maple K. Cibinetide: Unlocking the Potential of Peptide Therapy for Inflammation, Neuropathy, and Tissue Repair. 2024. [Medical Anti-Aging PDF]
Third-Party Testing Results
All products undergo rigorous third-party HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) testing to verify purity and quality.
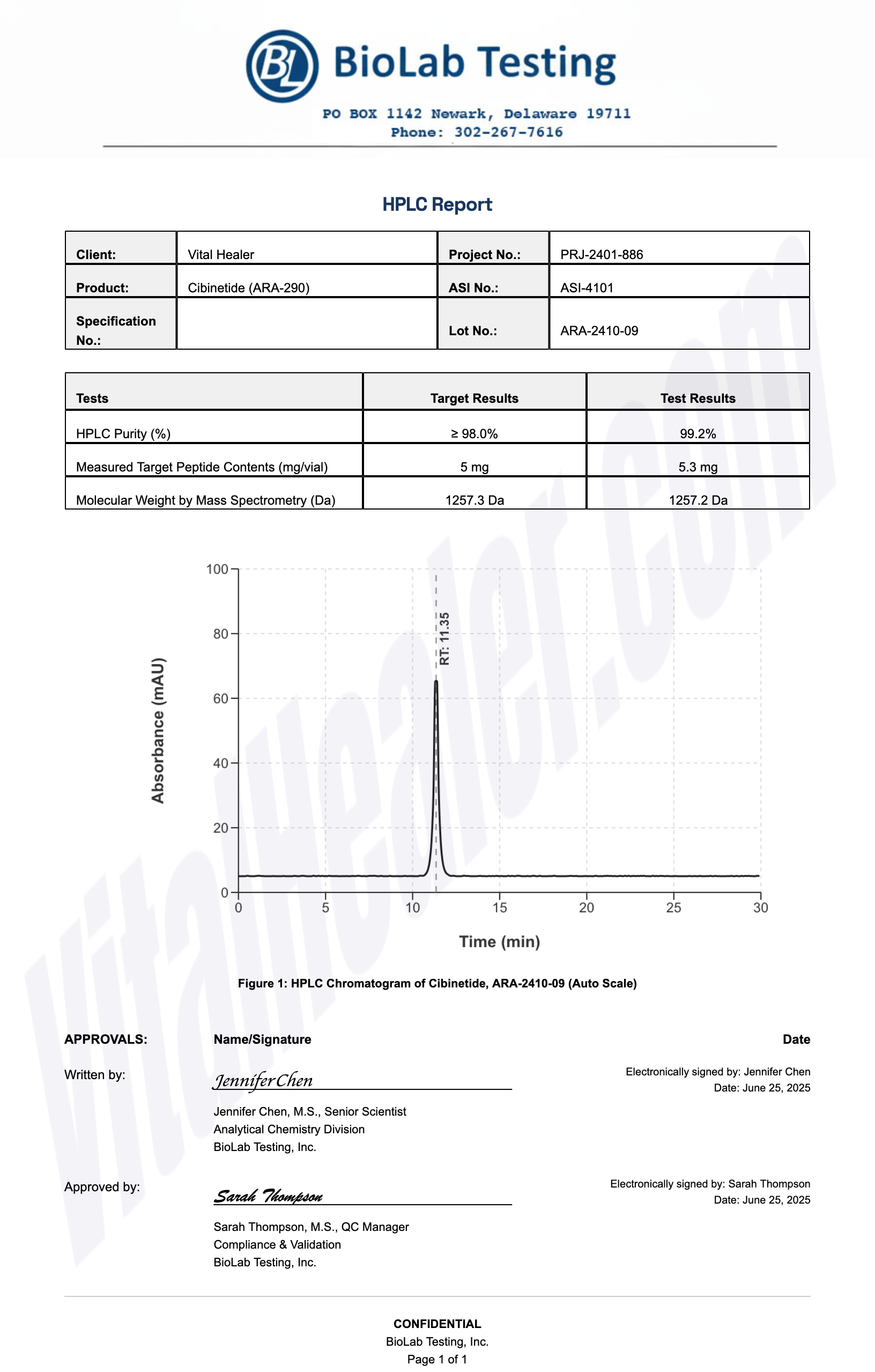
About HPLC Testing:
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a standard analytical technique used to verify peptide purity. Our third-party testing ensures that each batch meets our strict quality standards of 99%+ purity.
Related Research Peptides