Semaglutide
A synthetic GLP-1 receptor agonist investigated for metabolic research applications, including glucose regulation, appetite modulation, and weight management.
Key Research Properties:
| SKU: | semaglutide |
|---|---|
| Purity: | >99% (HPLC Verified) |
| Form: | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C |
| CAS Number: | 910463-68-2 |
| Lot Number: | SEM-2410-05: 2mg, 5mg, 10mg |
All products are sold strictly for laboratory and research purposes. Products are not intended for human use or consumption of any kind.
The statements presented on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or disease.
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a synthetic GLP-1 receptor agonist that has become one of the most extensively studied peptides in metabolic research. Originally developed for type 2 diabetes management, semaglutide has gained significant attention for its profound effects on weight loss, making it a focal point of obesity and metabolic disorder research[1].
Semaglutide shares 94% structural homology with native human GLP-1 but incorporates strategic modifications that dramatically extend its half-life from approximately 2 minutes (for native GLP-1) to roughly 7 days. This is achieved through amino acid substitutions and the attachment of a C-18 fatty diacid chain via a spacer, which enables albumin binding and protects against dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) degradation[2].
Development History
Semaglutide was developed by Novo Nordisk as part of their incretin-based therapy program. Following extensive preclinical development, it entered clinical trials in the early 2010s:
- 2012-2016: Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials (SUSTAIN program) for type 2 diabetes[3]
- 2017: FDA approval for type 2 diabetes (Ozempic®, 0.5-1.0 mg weekly)
- 2018-2020: STEP trial program investigating higher doses (2.4 mg) for weight management[4]
- 2021: FDA approval for chronic weight management (Wegovy®, 2.4 mg weekly)
- 2023: SELECT cardiovascular outcomes trial demonstrated 20% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events[5]
Molecular Characteristics
| Molecular Formula | C₁₈₇H₂₉₁N₄₅O₅₉ |
| Molecular Weight | 4,113.58 g/mol |
| Sequence | 31 amino acids with modifications at positions 8 and 26, plus C-18 fatty diacid chain |
| Half-Life | ~7 days (vs. ~2 min for native GLP-1) |
| Bioavailability | 89% (subcutaneous injection) |
| Storage | 2-8°C (refrigerated), protect from light |
Key Research Findings
Semaglutide represents one of the most successful therapeutic developments in metabolic research:
- Weight Loss: STEP trials demonstrated 15-20% body weight reduction at 2.4 mg weekly, significantly superior to prior GLP-1 agonists[4]
- Glycemic Control: HbA1c reductions of 1.5-2.0% in diabetes trials, with sustained effects over 2+ years[3]
- Cardiovascular Benefits: 20% reduction in MACE (major adverse cardiovascular events) in high-risk populations[5]
- Metabolic Improvements: Reductions in blood pressure, inflammatory markers, and liver fat content[6]
Research Grade vs. Pharmaceutical Grade
While pharmaceutical semaglutide (Ozempic®, Wegovy®) is FDA-approved for clinical use, research-grade semaglutide is intended exclusively for laboratory and in-vitro research purposes. Our product is not intended for human consumption or therapeutic use. All research should be conducted by qualified personnel in appropriate laboratory settings following institutional guidelines.
How Semaglutide Works
Semaglutide exerts its effects through activation of GLP-1 receptors, which are widely distributed throughout the body. The peptide's mechanism is multifaceted, affecting glucose homeostasis, appetite regulation, gastric motility, and cardiovascular function[7].
GLP-1 Receptor Activation
Semaglutide is a high-affinity agonist of the GLP-1 receptor, a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) belonging to the class B family. Upon binding, semaglutide triggers multiple intracellular signaling cascades including Gs/cAMP/PKA pathway, EPAC2 activation, and PI3K/Akt signaling[2].
Pancreatic Effects
In pancreatic beta cells, semaglutide enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion through increased intracellular calcium, improved insulin biosynthesis, and beta cell protection. It also optimizes insulin-to-glucose regulatory balance[8].
Central Nervous System Effects
Semaglutide crosses the blood-brain barrier and acts on hypothalamic appetite centers, activating POMC neurons while inhibiting NPY/AgRP neurons. This leads to reduced appetite and increased satiety. It also affects reward centers, reducing food cravings[9].
Gastrointestinal Effects
Semaglutide delays gastric emptying by 70-80 minutes, reducing postprandial glucose excursions and prolonging satiety. It also slows intestinal transit[10].
Cardiovascular & Hepatic Effects
GLP-1 receptors on cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and hepatocytes mediate cardioprotective effects, improved endothelial function, reduced hepatic steatosis, and decreased systemic inflammation[5][11].
Extended Half-Life Modifications
Semaglutide's C-18 fatty acid chain binds reversibly to serum albumin, creating a circulating reservoir. Combined with DPP-4 resistance from amino acid substitutions, this extends half-life to ~165 hours, enabling once-weekly dosing.
Research Applications
Semaglutide has become one of the most extensively studied peptides in metabolic research, with over 10,000 participants enrolled in clinical trials spanning diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease, and emerging applications[12].
Obesity and Weight Management Research
The STEP program represents the most comprehensive weight loss research for any GLP-1 agonist[4]:
- STEP 1 (n=1,961): 2.4 mg weekly achieved 14.9% weight loss vs. 2.4% placebo at 68 weeks
- STEP 2 (n=1,210): In patients with type 2 diabetes, 9.6% weight loss with HbA1c improvements
- STEP 3-5: Combined behavioral therapy, withdrawal studies, and 104-week sustained effects
Type 2 Diabetes Research
The SUSTAIN program evaluated semaglutide across diverse diabetic populations[3]:
- SUSTAIN 1-5: Head-to-head trials showing superior HbA1c reductions (1.5-1.8%)
- SUSTAIN 6: Cardiovascular outcomes trial with 26% reduction in 3-point MACE
- SUSTAIN 7: Direct comparison with dulaglutide demonstrating superior efficacy
Cardiovascular Research
The SELECT trial revolutionized understanding of obesity as a cardiovascular risk factor[5]:
- Study: 17,604 participants with established CVD and BMI ≥27, followed 33.7 months
- Results: 20% reduction in 3-point MACE, 19% reduction in CV death, 28% reduction in heart failure events
NASH & Kidney Disease
Emerging research explores hepatic and renal applications[11][13]:
- NASH: 72-week study showed 59% resolution vs. 17% placebo, 55% hepatic fat reduction
- FLOW Trial: 24% reduction in composite renal outcomes, slowed eGFR decline
Neurodegenerative Disease Research
Preclinical and early clinical research explores neuroprotective potential in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease through reduced neuroinflammation and improved mitochondrial function[14].
Research vs. Clinical Use
The research findings described here pertain to pharmaceutical-grade semaglutide used in controlled clinical trials. Research-grade peptides are for laboratory use only and not approved for human consumption.
Research Dosing Protocols
Published research protocols for semaglutide follow carefully designed dose escalation schedules to minimize gastrointestinal side effects while achieving therapeutic objectives[3][4].
For Research Purposes Only
The dosing information presented here is derived from published clinical research and is provided solely for educational and laboratory research purposes. This product is not intended for human use or consumption. Research must be conducted by qualified personnel following institutional review board (IRB) approval.
Standard Dose Escalation Schedule
Clinical trials employed gradual dose escalation to minimize adverse effects:
| Weeks | Dose (subcutaneous, weekly) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1-4 | 0.25 mg | Initial tolerance assessment |
| 5-8 | 0.5 mg | First escalation |
| 9-12 | 1.0 mg | Diabetes maintenance dose |
| 13-16 | 1.7 mg | Intermediate dose |
| 17+ | 2.4 mg | Target dose for weight management |
Application-Specific Protocols
Type 2 Diabetes Research (SUSTAIN Trials)
- Maintenance Dose: 0.5 mg or 1.0 mg weekly
- Escalation: 4 weeks at 0.25 mg, then increase to maintenance
- Duration: Trials ranged from 30 weeks to 104 weeks
Weight Management Research (STEP Trials)
- Target Dose: 2.4 mg weekly
- Escalation: 16-20 week ramp-up through all dose levels
- Duration: Primary endpoints at 68 weeks; some trials extended to 104 weeks
- Adjunct: Combined with reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity
Reconstitution for Research
Research-grade semaglutide supplied as lyophilized powder requires reconstitution:
- Solvent: Bacteriostatic water for injection or sterile water
- Technique: Add solvent slowly down vial wall; swirl gently (do not shake)
- Storage Post-Reconstitution: 2-8°C, use within 4 weeks
- Stability: Protect from light; do not freeze
Pharmacokinetics Summary
| Tmax (time to peak) | 1-3 days post-injection |
| Half-life | ~7 days (165 hours) |
| Steady State | 4-5 weeks of weekly dosing |
| Bioavailability | 89% (subcutaneous) |
| Protein Binding | >99% (primarily albumin) |
Research Protocol Design
When designing in-vitro or preclinical research protocols, consider the extended half-life and slow onset of action. Steady-state conditions require 4-5 weeks of dosing. Always consult published literature for your specific research model and application.
Safety Profile & Side Effects
Semaglutide has been extensively evaluated in clinical trials involving over 10,000 participants. While pharmaceutical-grade semaglutide is FDA-approved with a well-characterized safety profile, this information is provided for research reference only. Research-grade semaglutide is not approved for human use.
Critical Safety Notice
This product is sold strictly for laboratory research purposes. It is NOT intended for human consumption, therapeutic use, or any application outside of controlled research settings.
Most Common Adverse Events
Based on pooled data from STEP and SUSTAIN trials[15]:
| Adverse Event | Semaglutide 2.4 mg | Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea | 44% | 17% |
| Diarrhea | 31% | 16% |
| Vomiting | 24% | 8% |
| Constipation | 24% | 11% |
| Abdominal Pain | 20% | 12% |
Serious Adverse Events
Gastrointestinal
- Pancreatitis: 0.2% incidence. Symptoms include severe persistent abdominal pain radiating to back[15]
- Gallbladder Disease: 2.8% vs. 1.7% placebo. Risk increased with rapid weight loss[16]
- Gastroparesis: Rare but documented cases of severe delayed gastric emptying
Hypoglycemia
- Monotherapy: <1% (similar to placebo) due to glucose-dependent mechanism
- With Insulin/Sulfonylureas: 15-20% clinically significant hypoglycemia
Thyroid C-Cell Tumors
- Preclinical Concern: Rodent studies showed dose-dependent thyroid C-cell tumors
- Clinical Data: No confirmed cases of medullary thyroid carcinoma in human trials to date
- Black Box Warning: FDA-mandated warning regarding thyroid C-cell tumor risk[17]
Discontinuation Rates
Across major trials[4]:
- Overall: 7-11% due to adverse events (vs. 3-4% placebo)
- Primary Reason: Gastrointestinal events (5-7%)
- Timing: Most discontinuations during dose escalation (weeks 0-20)
Contraindications & Warnings
Absolute Contraindications
- Personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC)
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2)
- History of serious hypersensitivity to semaglutide
- Pregnancy (teratogenic in animal studies)
Warnings & Precautions
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Rapid glucose reduction may temporarily worsen retinopathy[18]
- Renal Impairment: Use cautiously in severe impairment (eGFR <30)
- Drug Interactions: Delayed gastric emptying may affect absorption of oral medications
Long-Term Safety Data
Studies up to 104 weeks have shown:
- No new safety signals emerging after first year
- GI side effects diminish substantially after 6-12 months
- Cardiovascular benefits sustained (SELECT trial: median 33.7 months)
- Bone mineral density stable
Safety Monitoring in Research
Clinical trials employed comprehensive safety monitoring including vital signs, ECG, metabolic panels, lipase/amylase testing, and periodic calcitonin measurements. Any preclinical or in-vitro research should incorporate appropriate safety assessments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Clinical Trials
Semaglutide is one of the most extensively studied GLP-1 receptor agonists, with over 100 registered clinical trials evaluating its effects on type 2 diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular outcomes, and other metabolic conditions. This tab summarizes key clinical trial programs and provides resources for finding additional studies.
STEP Program: Weight Management Trials
The Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity (STEP) clinical trial program evaluated semaglutide 2.4 mg weekly for chronic weight management in adults with overweight or obesity.
STEP 1 (NCT03548935)
Study Title: "Semaglutide vs Placebo in Adults With Overweight or Obesity (STEP 1)"
Status: Completed
Phase: Phase 3
Enrollment: 1,961 participants
Study Period: 2018-2020
Location: 16 countries, 129 sites
Design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
Duration: 68 weeks
Intervention: Semaglutide 2.4 mg SC weekly + lifestyle intervention
Population: Adults with BMI ≥30 or ≥27 with comorbidity, no diabetes
Key Results:
- Mean Weight Loss: 14.9% with semaglutide vs. 2.4% with placebo
- ≥5% Weight Loss: 86.4% vs. 31.5% (placebo)
- ≥15% Weight Loss: 50.5% vs. 4.9% (placebo)
- Cardiometabolic Improvements: Reductions in waist circumference, blood pressure, lipids, inflammatory markers, and HbA1c in participants with prediabetes
- Safety: Most common adverse events were gastrointestinal (nausea 44%, diarrhea 30%); generally mild-moderate
Publication: Wilding JPH, et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002.
STEP 2 (NCT03552757)
Study Title: "Semaglutide in Adults With Overweight or Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes (STEP 2)"
Status: Completed
Phase: Phase 3
Enrollment: 1,210 participants
Study Period: 2018-2020
Design: Randomized, double-blind, active-controlled
Duration: 68 weeks
Intervention: Semaglutide 2.4 mg vs. 1.0 mg vs. placebo + lifestyle
Population: Adults with BMI ≥27 and type 2 diabetes
Key Results:
- Mean Weight Loss: 9.6% (2.4 mg) vs. 7.0% (1.0 mg) vs. 3.4% (placebo)
- ≥10% Weight Loss: 45.6% (2.4 mg) vs. 28.7% (1.0 mg) vs. 8.2% (placebo)
- HbA1c Reduction: 1.6% (2.4 mg) vs. 1.5% (1.0 mg) vs. 0.4% (placebo)
- Glycemic Control: 68% (2.4 mg) achieved HbA1c <7%
- Clinical Significance: Demonstrated dose-dependent weight loss and glycemic benefits in people with T2D
Publication: Davies M, et al. Lancet. 2021;397(10278):971-984.
Additional STEP Trials
| Trial | Population | Key Finding | NCT Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| STEP 3 | Adults with overweight/obesity + intensive behavioral therapy | 16.0% mean weight loss vs. 5.7% (placebo) at 68 weeks | NCT03611582 |
| STEP 4 | Weight loss maintenance after initial 20-week run-in | 7.9% additional loss (continued) vs. 6.9% weight regain (switch to placebo) | NCT03548987 |
| STEP 5 | Long-term (104 weeks) efficacy and safety | 15.2% mean weight loss maintained over 2 years | NCT03693430 |
| STEP 6 | East Asian population with overweight/obesity | 13.2% mean weight loss; similar efficacy in Asian populations | NCT03811574 |
| STEP 8 | Head-to-head vs. liraglutide 3.0 mg | 15.8% (semaglutide) vs. 6.4% (liraglutide) at 68 weeks | NCT03548987 |
SUSTAIN Program: Type 2 Diabetes Trials
The SUSTAIN (Semaglutide Unabated Sustainability in Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes) program evaluated semaglutide 0.5 mg and 1.0 mg weekly for glycemic control in type 2 diabetes.
| Trial | Comparator | Duration | Key Results (HbA1c Reduction) | NCT Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUSTAIN 1 | Placebo (monotherapy) | 30 weeks | 1.5% (1.0 mg) vs. 1.2% (0.5 mg) vs. placebo; weight loss 3.7-4.5 kg | NCT02054897 |
| SUSTAIN 2 | Sitagliptin 100 mg | 56 weeks | 1.3% (1.0 mg) vs. 1.1% (0.5 mg) vs. 0.5% (sitagliptin) | NCT01930188 |
| SUSTAIN 3 | Exenatide ER 2 mg | 56 weeks | 1.5% (1.0 mg) vs. 1.4% (0.5 mg) vs. 0.9% (exenatide ER); superior weight loss | NCT01885208 |
| SUSTAIN 4 | Insulin glargine | 30 weeks | 1.6% (1.0 mg) vs. 1.4% (0.5 mg) vs. 0.8% (insulin glargine); weight gain with insulin | NCT02128932 |
| SUSTAIN 5 | Placebo (add-on to basal insulin) | 30 weeks | 1.4% (1.0 mg) vs. 1.2% (0.5 mg) vs. placebo; added to existing insulin therapy | NCT02305381 |
| SUSTAIN 6 | Placebo (CV outcomes) | 104 weeks | 26% reduction in 3-point MACE; diabetic retinopathy concerns noted | NCT01720446 |
| SUSTAIN 7 | Dulaglutide 1.5 mg | 40 weeks | 1.8% (1.0 mg) vs. 1.6% (0.5 mg) vs. 1.4% (dulaglutide); superiority shown | NCT02648204 |
| SUSTAIN 8 | Canagliflozin 300 mg | 52 weeks | 1.5% (1.0 mg) vs. 1.0% (canagliflozin); GLP-1 RA superior for HbA1c | NCT03136484 |
| SUSTAIN 9 | Placebo (add-on to SGLT2i) | 30 weeks | 1.5% (1.0 mg) vs. 1.2% (0.5 mg) vs. placebo; combination with SGLT2i effective | NCT03086330 |
| SUSTAIN 10 | Liraglutide 1.2 mg | 30 weeks | 1.7% (1.0 mg) vs. 1.0% (liraglutide); non-inferiority and superiority shown | NCT03191396 |
SELECT: Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial
SELECT (NCT03574597)
Study Title: "Semaglutide Effects on Heart Disease and Stroke in Patients with Overweight or Obesity"
Status: Completed
Phase: Phase 3
Enrollment: 17,604 participants
Study Period: 2018-2023
Location: 804 sites in 41 countries
Design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled event-driven trial
Duration: Median 39.8 months
Intervention: Semaglutide 2.4 mg SC weekly vs. placebo
Population: Adults ≥45 years with BMI ≥27 and established cardiovascular disease
Key Results (Published August 2023):
- Primary Endpoint (3-point MACE): 20% relative risk reduction (HR 0.80, 95% CI 0.72-0.90, p<0.001)
- CV Death: 15% reduction (not statistically significant)
- Non-Fatal MI: 28% reduction (p<0.001)
- Non-Fatal Stroke: 7% reduction (not significant)
- Weight Loss: 9.4% mean reduction vs. 0.9% with placebo
- Clinical Significance: First obesity treatment to show cardiovascular benefit; paradigm shift in obesity as cardiovascular risk factor management
Publication: Lincoff AM, et al. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(24):2221-2232.
Ongoing & Emerging Research
Alzheimer's Disease (EVOKE/EVOKE Plus)
Status: Phase 3 Ongoing
Focus: Oral semaglutide for prevention of Alzheimer's disease
Population: Adults with early Alzheimer's disease
Timeline: Results expected 2025-2026
Chronic Kidney Disease (FLOW)
Status: Completed (results pending publication)
Focus: Kidney outcomes in type 2 diabetes with CKD
Population: T2D patients with CKD (eGFR 25-75)
Timeline: Trial stopped early due to efficacy; publication expected 2024
NASH/MASH
Status: Phase 3 Ongoing
Focus: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) treatment
Population: Adults with biopsy-confirmed NASH
Timeline: Multiple trials evaluating hepatic outcomes
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Status: Phase 3 Ongoing
Focus: OSA improvement in obese patients
Population: Adults with OSA and obesity
Timeline: Results expected 2024-2025
Research Resources
How to Find More Trials
1. ClinicalTrials.gov
2. PubMed
3. Key Research Institutions
- University College London (Prof. Rachel Batterham - STEP trials)
- Cleveland Clinic (SELECT trial)
- Yale University (Dr. Silvio Inzucchi - SUSTAIN trials)
- Novo Nordisk (trial sponsor and developer)
References & Citations
The following peer-reviewed publications and clinical trial data support the research information presented on this page.
- Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
- Lau J, Bloch P, Schäffer L, et al. Discovery of the Once-Weekly GLP-1 Analogue Semaglutide. J Med Chem. 2015;58(18):7370-7380. PMID: 26308095
- Sorli C, Harashima SI, Tsoukas GM, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide monotherapy versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 1). Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(4):251-260. PMID: 28110911
- Rubino D, Abrahamsson N, Davies M, et al. Effect of Continued Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Placebo on Weight Loss Maintenance in Adults With Overweight or Obesity: The STEP 4 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021;325(14):1414-1425. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2777886
- Lincoff AM, Brown-Frandsen K, Colhoun HM, et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(24):2221-2232. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2307563
- Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Davies M, et al. Weight regain and cardiometabolic effects after withdrawal of semaglutide: The STEP 1 trial extension. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022;24(8):1553-1564. PMID: 35441470
- Drucker DJ. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of GLP-1. Cell Metab. 2018;27(4):740-756. PMC5975840
- Nauck MA, Meier JJ. GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: a review of head-to-head clinical studies. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23 Suppl 3:3-18. PMID: 34310013
- van Bloemendaal L, IJzerman RG, Ten Kulve JS, et al. GLP-1 receptor activation modulates appetite- and reward-related brain areas in humans. Diabetes. 2014;63(12):4186-4196. PMID: 25071023
- Friedrichsen M, Breitschaft A, Tadayon S, Wizert A, Skovgaard D. The effect of semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly on energy intake, appetite, control of eating, and gastric emptying in adults with obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23(3):754-762. PMID: 33269535
- Newsome PN, Buchholtz K, Cusi K, et al. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(12):1113-1124. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2028395
- Davies M, Færch L, Jeppesen OK, et al. Semaglutide 2·4 mg once a week in adults with overweight or obesity, and type 2 diabetes (STEP 2). Lancet. 2021;397(10278):971-984. PMID: 33667417
- Perkovic V, Tuttle KR, Rossing P, et al. Effects of Semaglutide on Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2024;391(2):109-121. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2403347
- Gejl M, Gjedde A, Egefjord L, et al. In Alzheimer's Disease, 6-Month Treatment with GLP-1 Analog Prevents Decline of Brain Glucose Metabolism. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016;8:108. PMC4870944
- Wadden TA, Bailey TS, Billings LK, et al. Effect of Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Placebo as an Adjunct to Intensive Behavioral Therapy on Body Weight in Adults With Overweight or Obesity: The STEP 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021;325(14):1403-1413. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2777825
- Nauck MA, Muus Ghorbani ML, Kreiner E, Eckel RH. Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on gallbladder disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23(7):1461-1470. PMID: 33650287
- Gier B, Matveyenko AV, Kirakossian D, et al. Chronic GLP-1 receptor activation by exendin-4 induces expansion of pancreatic duct glands in rats. Diabetes. 2012;61(5):1250-1262. PMC3331773
- Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(19):1834-1844. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa1607141
Additional Resources
For comprehensive research data on semaglutide:
- ClinicalTrials.gov: Search "semaglutide" for ongoing and completed trials
- PubMed: Database of biomedical literature (National Library of Medicine)
- Cochrane Library: Systematic reviews of GLP-1 receptor agonists
Third-Party Testing Results
All products undergo rigorous third-party HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) testing to verify purity and quality.
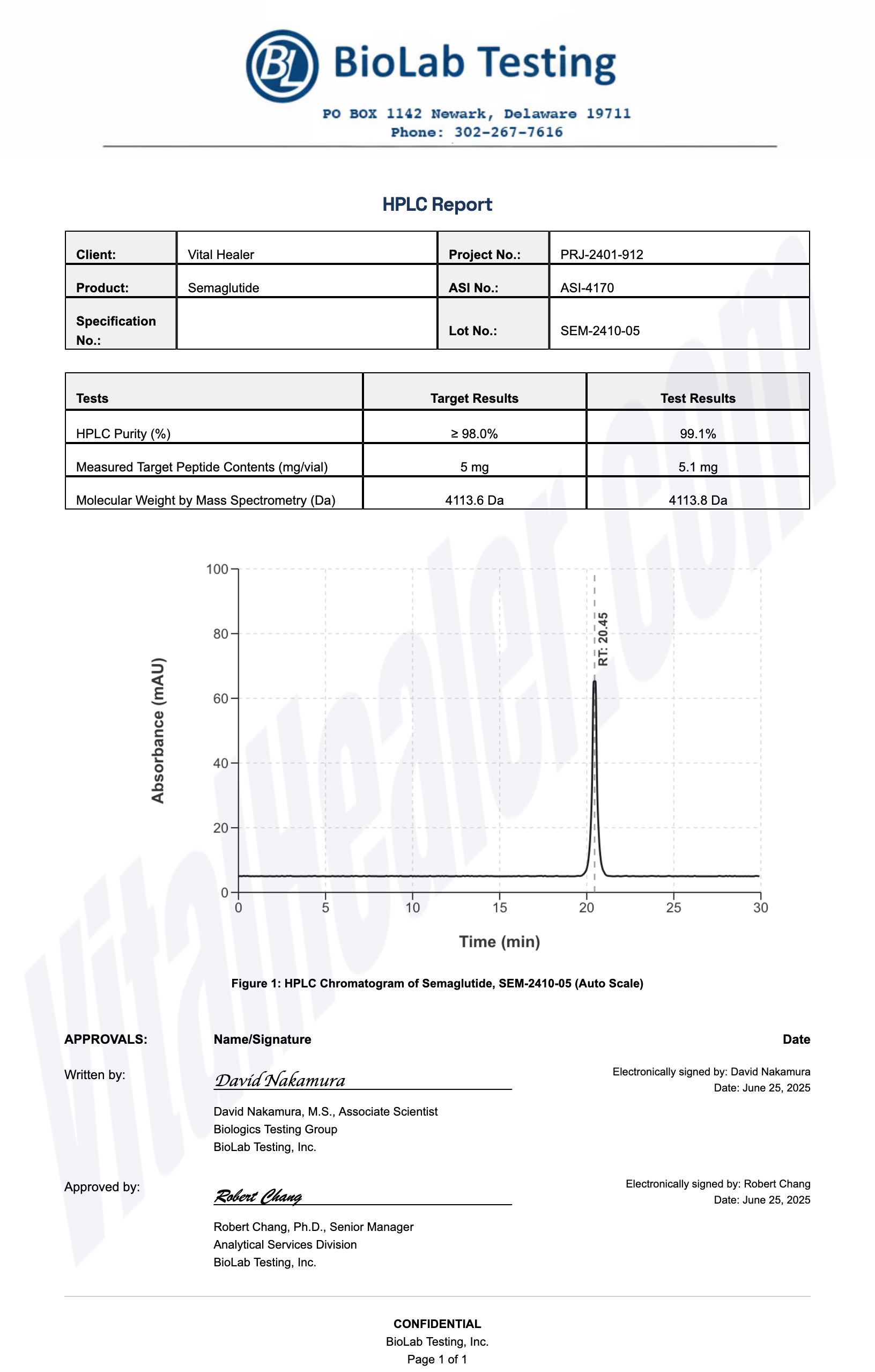
About HPLC Testing:
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a standard analytical technique used to verify peptide purity. Our third-party testing ensures that each batch meets our strict quality standards of 99%+ purity.
Related Research Peptides