Cagrilintide
A long-acting amylin receptor agonist investigated for weight management. Synergistic with GLP-1 agonists - the CagriSema combination (cagrilintide + semaglutide) shows 15.6% weight loss.
Key Research Properties:
| SKU: | cagrilintide |
|---|---|
| Purity: | >99% (HPLC Verified) |
| Form: | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C |
| CAS Number: | 1415456-99-3 |
| Lot Number: | CAG-2410-03: 5mg, 10mg |
All products are sold strictly for laboratory and research purposes. Products are not intended for human use or consumption of any kind.
The statements presented on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or disease.
What is Cagrilintide?
Cagrilintide is a long-acting amylin receptor agonist developed by Novo Nordisk for metabolic research applications. This investigational peptide mimics the natural hormone amylin (also known as islet amyloid polypeptide or IAPP), which plays a crucial role in glucose homeostasis and satiety regulation[1].
Unlike native amylin, which has an extremely short half-life of minutes, cagrilintide has been engineered for once-weekly subcutaneous administration through strategic amino acid substitutions and fatty acid acylation. This extended pharmacokinetic profile makes it particularly suitable for long-term metabolic research studies[2].
Cagrilintide (Long-Acting Amylin Analog)
- Amino acid sequence modified from native human amylin[3]
- Fatty acid acylation extends half-life to approximately 7 days[2]
- Selective amylin receptor agonist (AMY1, AMY2, AMY3)[4]
- Delays gastric emptying and reduces food intake[5]
- Controls postprandial glucose metabolism[6]
- Synergistic effects with GLP-1 receptor agonists[7]
CagriSema: The Synergistic Combination
One of the most significant developments in cagrilintide research is its combination with semaglutide (a GLP-1 receptor agonist), known as CagriSema. This fixed-ratio combination leverages complementary mechanisms of action to produce superior metabolic effects compared to either agent alone[7]:
| Study | Treatment | Mean Weight Loss | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| STEP 1[8] | Semaglutide 2.4 mg | -14.9% | 68 weeks |
| REDEFINE 1[7] | CagriSema (2.4 mg/2.4 mg) | -15.6% | 32 weeks |
| Phase 2[9] | Cagrilintide 2.4 mg | -10.8% | 32 weeks |
The CagriSema combination demonstrates that dual targeting of amylin and GLP-1 receptors produces additive or synergistic effects, representing a promising avenue for advanced metabolic research[7].
Molecular & Chemical Information
| Property | Cagrilintide |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C₁₉₁H₂₉₀N₅₀O₅₆S (approximate) |
| Molecular Weight | ~4326 Da |
| CAS Number | 1415456-99-3 |
| Half-Life | ~155 hours (6.5 days)[2] |
| Receptor Target | Amylin receptors (AMY1, AMY2, AMY3) |
| Modification | Fatty acid acylated analog of human amylin |
| Administration Route | Subcutaneous injection |
Background: Amylin's Physiological Role
Amylin is a 37-amino acid peptide hormone co-secreted with insulin from pancreatic β-cells in response to nutrient ingestion. In healthy individuals, amylin:insulin molar ratio is approximately 1:100[10].
Amylin's primary physiological functions include[11]:
- Slowing gastric emptying: Delays the rate at which food enters the small intestine, reducing post-meal glucose spikes
- Controlling glucose metabolism: Reduces inappropriate hepatic glucose output during meals
- Promoting satiety: Acts on area postrema in the brainstem to reduce food intake
In type 2 diabetes, amylin secretion is impaired alongside insulin deficiency, contributing to postprandial hyperglycemia and dysregulated satiety[12]. Cagrilintide was developed to restore and enhance these amylinomimetic effects with a more convenient dosing schedule than pramlintide (the first-generation amylin analog requiring multiple daily injections).
How Cagrilintide Works
Cagrilintide functions as a selective amylin receptor agonist, mimicking and amplifying the physiological effects of endogenous amylin. Its mechanism of action involves multiple complementary pathways that collectively regulate glucose homeostasis, gastric function, and energy balance[4].
Amylin Receptor Activation
Amylin receptors are heterodimeric complexes formed by the calcitonin receptor (CTR) paired with receptor activity-modifying proteins (RAMPs). Three principal amylin receptor subtypes exist[13]:
AMY1 Receptor
CTR + RAMP1
Primary receptor in area postrema (brainstem satiety center)[14]
AMY2 Receptor
CTR + RAMP2
Expressed in cardiovascular tissues and central nervous system[14]
AMY3 Receptor
CTR + RAMP3
Found in peripheral tissues including gastrointestinal tract[14]
Cagrilintide binds to and activates these receptors with high affinity, triggering intracellular signaling cascades involving cyclic AMP (cAMP) and calcium mobilization[4].
Delayed Gastric Emptying
One of cagrilintide's most pronounced effects is slowing the rate of gastric emptying through activation of amylin receptors in the area postrema and vagal afferent pathways[5]:
- Central Nervous System Signaling: Activation of AMY1 receptors in the area postrema initiates vagal efferent signals that reduce gastric motility and pyloric relaxation[15]
- Direct Peripheral Effects: AMY3 receptor activation in the stomach and proximal small intestine may contribute to local motor function regulation[16]
- Metabolic Consequences: Delayed gastric emptying reduces the rate of glucose appearance in the bloodstream, lowering postprandial glucose excursions without increasing insulin demand[5]
In Phase 2 trials, cagrilintide demonstrated dose-dependent reductions in gastric emptying rate, with effects sustained over the week-long dosing interval[9].
Hepatic Glucose Regulation
Cagrilintide controls inappropriate postprandial hepatic glucose output. This effect is particularly relevant in metabolic research contexts where metabolic imbalance contributes to hyperglycemia[6]:
Mechanism of Glucose Control
The exact mechanisms remain under investigation, but evidence suggests:
- Direct effects on pancreatic cells via local amylin receptor activation
- Indirect modulation through delayed nutrient absorption (slower gastric emptying)
- Central nervous system-mediated effects on metabolic regulation[6]
By reducing hepatic glucose output during the postprandial period, cagrilintide decreases glucose production, contributing to improved glycemic control independent of its effects on insulin secretion[6].
Satiety and Food Intake Reduction
Cagrilintide's most clinically significant effect is its potent reduction in food intake and enhancement of satiety through activation of AMY1 receptors in the area postrema[14]:
- Brainstem Satiety Signaling: Area postrema neurons project to nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS), which integrates peripheral satiety signals and regulates feeding behavior[17]
- Dose-Dependent Effects: Higher doses of cagrilintide produce greater reductions in ad libitum food intake and increased subjective fullness ratings[9]
- Sustained Effect: Unlike acute satiety signals, cagrilintide's long half-life provides continuous appetite suppression between weekly doses[2]
Synergy with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
The combination of cagrilintide with GLP-1 receptor agonists (particularly semaglutide) produces effects greater than either agent alone. This synergy operates through multiple mechanisms[7]:
| Pathway | Cagrilintide (Amylin Agonist) | Semaglutide (GLP-1 Agonist) | Combined Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric Emptying | Marked delay via area postrema | Moderate delay via vagal pathways | Synergistic slowing |
| Satiety Signaling | Area postrema → NTS pathway | Hypothalamic POMC/CART neurons | Complementary CNS targets |
| Hepatic Glucose | Postprandial reduction | Glucose-dependent suppression | Enhanced glycemic control |
| Insulin | No direct effect | Glucose-dependent secretion | Preserved insulin response |
The REDEFINE 1 trial demonstrated that CagriSema (cagrilintide 2.4 mg + semaglutide 2.4 mg) produced 15.6% weight loss compared to 10.8% with cagrilintide alone and historical data of ~15% with semaglutide alone, suggesting true synergy[7].
Research Applications & Contexts
Cagrilintide is being investigated across multiple research contexts focused on metabolic regulation, weight management, and glucose homeostasis. As an investigational peptide with extensive clinical trial data, it offers researchers a well-characterized tool for studying amylin receptor biology[18].
1. Obesity and Weight Management Research
The primary focus of cagrilintide research has been its profound effects on body weight reduction[9]:
- Design: 32-week, dose-ranging study in 706 adults with overweight/obesity
- Results (Cagrilintide monotherapy):[9]
- 0.3 mg weekly: -3.9% weight loss
- 0.6 mg weekly: -6.0% weight loss
- 1.2 mg weekly: -8.1% weight loss
- 2.4 mg weekly: -10.8% weight loss
- 4.5 mg weekly: -10.4% weight loss
- Mechanism: Weight loss attributed primarily to reduced energy intake (-535 kcal/day at 2.4 mg dose) rather than increased energy expenditure
Research Implications: Cagrilintide provides a valuable research tool for investigating amylin receptor-mediated satiety pathways independent of GLP-1 signaling, offering insights into hormone-specific contributions to appetite regulation.
2. Combination Therapy Research (CagriSema)
The synergistic combination of cagrilintide with semaglutide represents a novel approach in multi-agonist metabolic therapeutics[7]:
Primary Efficacy
- CagriSema: -15.6% weight loss at 32 weeks[7]
- Cagrilintide alone: -10.8%
- Placebo: -2.4%
Responder Rates
- ≥10% weight loss: 74% (CagriSema)
- ≥15% weight loss: 52% (CagriSema)
- ≥20% weight loss: 32% (CagriSema)
Research Applications:
- Investigation of multi-receptor agonism strategies in metabolic regulation
- Study of synergistic vs. additive effects in combination pharmacology
- Exploration of complementary satiety pathway activation
- Analysis of dose optimization in fixed-ratio combinations
3. Glucose Homeostasis and Diabetes Research
While primarily studied for weight management, cagrilintide demonstrates significant effects on glucose metabolism[6]:
- Postprandial Glucose Control: Cagrilintide reduces post-meal glucose excursions through delayed gastric emptying and hepatic glucose regulation[5]
- HbA1c Reduction: In subjects with type 2 diabetes, cagrilintide produces clinically meaningful reductions in HbA1c (-0.8% to -1.2% depending on dose)[9]
- Insulin-Independent Mechanisms: Unlike GLP-1 agonists that enhance insulin secretion, cagrilintide's glycemic effects operate primarily through hepatic glucose regulation and nutrient absorption delay
Research Focus: Cagrilintide offers researchers a unique tool to study amylin's role in glucose homeostasis independent of insulin-potentiating effects, enabling dissection of hormone-specific contributions to metabolic control.
4. Gastric Motility and Gastrointestinal Research
Cagrilintide's pronounced effects on gastric emptying make it valuable for studying gastrointestinal physiology[5]:
- Gastric Emptying Studies: Quantification of dose-response relationships between amylin receptor activation and gastric motor function
- Nutrient Sensing: Investigation of how delayed gastric emptying affects incretin secretion and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) responses
- Satiety Signaling: Exploration of the relationship between mechanical gastric distension, vagal signaling, and central satiety pathways
5. Neuroscience and Appetite Regulation Research
Cagrilintide's selective action on brainstem satiety circuits provides insights into neural control of feeding behavior[14]:
Central Nervous System Research Applications
- Area postrema neural activity mapping during amylin receptor activation
- Nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) connectivity and second-order satiety neuron activation
- Integration of peripheral satiety signals (amylin, GLP-1, PYY, leptin) in feeding circuits
- Neuroplasticity changes in satiety pathways with chronic amylin agonist exposure[17]
6. Pharmacokinetic and Drug Development Research
Cagrilintide's molecular design exemplifies successful peptide engineering for extended duration of action[2]:
- Fatty Acid Acylation: Study of how lipid conjugation affects peptide pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, and albumin binding
- Receptor Selectivity: Investigation of structure-activity relationships for amylin receptor subtype selectivity
- Formulation Science: Development of stable peptide formulations for long-term storage and delivery
Comparative Research Context
| Amylin Analog | Half-Life | Dosing Frequency | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native Amylin | ~13 minutes | Continuous (physiologic) | Endogenous hormone |
| Pramlintide | ~48 minutes | 3x daily with meals | FDA approved (2005) |
| Cagrilintide | ~155 hours | Once weekly | Phase 3 (investigational) |
Research Dosing Protocols
Cagrilintide has been studied across a range of doses in clinical research settings. Understanding the dose-response relationship is essential for designing appropriate research protocols[9].
Clinical Trial Dosing Ranges
| Dose (mg/week) | Weight Loss (32 weeks) | Key Observations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 mg | -3.9% | Minimal gastrointestinal side effects | [9] |
| 0.6 mg | -6.0% | Moderate efficacy, good tolerability | [9] |
| 1.2 mg | -8.1% | Clinically significant weight reduction | [9] |
| 2.4 mg | -10.8% | Optimal efficacy/tolerability balance | [9] |
| 4.5 mg | -10.4% | No additional benefit vs. 2.4 mg; increased GI events | [9] |
Dose Titration Schedules
Clinical trials have employed gradual dose escalation to minimize gastrointestinal side effects[9]:
| Weeks | Dose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 0-3 | 0.3 mg once weekly | Initial low dose |
| 4-7 | 0.6 mg once weekly | First escalation |
| 8-11 | 1.2 mg once weekly | Second escalation |
| 12-31 | 2.4 mg once weekly | Maintenance dose |
Rationale: Gradual titration allows tolerance development to gastrointestinal effects (particularly nausea) while building up to therapeutic doses. Each escalation step typically doubles the dose.
CagriSema Combination Dosing
When combined with semaglutide, cagrilintide is administered as a fixed-ratio combination[7]:
- Cagrilintide: 2.4 mg
- Semaglutide: 2.4 mg
- Administered as single weekly injection
- Separate titration of each component during escalation phase[7]
Combination Benefits
- Single injection improves convenience
- Fixed ratio ensures consistent synergy
- Combined titration minimizes side effects
- 15.6% mean weight loss at 32 weeks[7]
Reconstitution and Storage
Handling Guidelines for Research Applications
Reconstitution
- Use bacteriostatic water (0.9% benzyl alcohol) for multi-dose vials
- Sterile water for single-use applications
- Add solvent slowly down vial wall
- Gently swirl (do not shake) to dissolve
- Typical concentration: 1-5 mg/mL
Storage
- Lyophilized powder: Store at -20°C, protected from light
- Reconstituted solution: 2-8°C (refrigerate) for up to 28 days with bacteriostatic water
- Avoid: Freezing reconstituted solution
- Stability: Peptide is sensitive to heat and light
Administration Route and Pharmacokinetics
- Route: Subcutaneous injection (clinical trials used abdomen, thigh, or upper arm)[2]
- Absorption: Gradual absorption from subcutaneous depot; Tmax ~24-72 hours
- Half-Life: ~155 hours (6.5 days), enabling once-weekly dosing[2]
- Steady State: Achieved after approximately 4-5 weeks of weekly dosing
- Clearance: Primarily peptide degradation; no significant renal or hepatic metabolism
Special Research Considerations
Important Protocol Design Factors
- Long Half-Life: Effects persist for ~7 days; discontinuation requires >3 weeks for complete washout
- Gastric Effects: Profound slowing of gastric emptying may affect absorption of concomitant compounds
- Food Intake Reduction: Can produce caloric deficits of 500+ kcal/day; consider nutritional monitoring in long-term studies[9]
- Individual Variability: Response heterogeneity observed in clinical trials (some subjects non-responders)
Safety Profile & Adverse Events
Clinical trial data from Phase 2 studies involving over 700 participants provides insights into cagrilintide's safety profile. The most common adverse events are gastrointestinal in nature, consistent with its mechanism of action[9].
Most Common Adverse Events
| Adverse Event | Placebo | Cagrilintide 2.4 mg | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nausea | 15% | 51% | Mostly mild-moderate; transient[9] |
| Vomiting | 5% | 24% | Mostly mild; decreases over time |
| Diarrhea | 9% | 18% | Mild-moderate; self-limiting |
| Constipation | 3% | 14% | Mild; intermittent |
| Abdominal Pain | 4% | 10% | Mild |
| Injection Site Reactions | 2% | 8% | Mild; localized erythema/pruritus |
Key Observations:
- Gastrointestinal adverse events are dose-dependent and most pronounced during dose escalation
- Symptoms typically peak within the first 4-8 weeks and diminish with continued treatment as tolerance develops
- Slow titration (4-week intervals) significantly reduces the incidence and severity of GI events
- Most adverse events classified as mild to moderate in severity[9]
Discontinuation Rates
7.3%
Placebo discontinuation rate[9]
15.8%
Cagrilintide 2.4 mg (optimal dose)[9]
24.5%
Cagrilintide 4.5 mg (high dose)[9]
The majority of discontinuations due to adverse events occurred during the titration phase, with GI symptoms (nausea, vomiting) being the primary reasons.
Serious Adverse Events
1. Pancreatitis
While rare in trials, GLP-1 and amylin-based therapies carry theoretical pancreatitis risk. Any severe, persistent abdominal pain requires immediate evaluation.
2. Gastroparesis
Profound slowing of gastric emptying could potentially lead to severe gastroparesis, particularly at high doses or in susceptible individuals. Symptoms: severe nausea, vomiting, inability to tolerate oral intake.
3. Hypoglycemia (when combined with insulin/sulfonylureas)
Cagrilintide alone does not increase insulin secretion and has low intrinsic hypoglycemia risk. However, when combined with insulin or sulfonylureas, dose reduction of these agents may be necessary[6].
4. Calorie Restriction Consequences
Marked reductions in food intake (>500 kcal/day) may lead to nutritional deficiencies, loss of lean body mass, or metabolic complications if not properly monitored.
Laboratory and Metabolic Parameters
Clinical trials have monitored various metabolic and safety parameters[9]:
| Parameter | Observed Changes | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate | Slight increase (+2-4 bpm) | Consistent with weight loss; no concerning arrhythmias |
| Blood Pressure | Decrease (-3 to -5 mmHg systolic) | Beneficial; associated with weight loss |
| Lipase/Amylase | Mild transient elevations in some subjects | Generally asymptomatic; monitored for pancreatitis risk |
| HbA1c | Reduction of -0.8% to -1.2% (in subjects with T2D) | Clinically meaningful glycemic improvement[9] |
| Liver Enzymes | Improvement (reduced ALT/AST) | Consistent with reduced hepatic steatosis from weight loss |
Contraindications & Precautions
Research Protocol Exclusion Criteria (from clinical trials)
- History of pancreatitis (acute or chronic)
- Pre-existing gastroparesis or severe gastrointestinal disease
- Personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2)
- History of diabetic ketoacidosis
- Severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m²)
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding (amylin effects on fetal development unknown)
Drug Interactions
- Oral Medications: Delayed gastric emptying may affect absorption of oral drugs. Clinical trials monitored oral contraceptive efficacy and found no clinically significant interactions[9].
- Insulin/Sulfonylureas: May increase hypoglycemia risk; dose adjustment of glucose-lowering agents may be necessary[6].
- GLP-1 Agonists: Synergistic when combined (as in CagriSema); GI side effects may be additive during titration[7].
Long-Term Safety Data
Cagrilintide has been studied for up to 32 weeks in Phase 2 trials, with ongoing Phase 3 studies (REDEFINE program) investigating longer-term safety profiles[18]. Key long-term considerations under investigation:
- Sustained GI tolerability beyond 6 months
- Cardiovascular outcomes (ongoing dedicated CVOT study)
- Bone health impacts from rapid weight loss
- Gallbladder events (cholecystitis, cholelithiasis)
- Mental health and suicidality (regulatory requirement for all weight-loss agents)
Frequently Asked Questions
- Cagrilintide: Amylin receptor agonist; primarily slows gastric emptying and promotes satiety via brainstem pathways; ~10.8% weight loss monotherapy[9]
- Semaglutide: GLP-1 receptor agonist; enhances insulin secretion, controls hepatic glucose output, and promotes satiety via hypothalamic pathways; ~14.9% weight loss[8]
- CagriSema (combination): Synergistic effects produce 15.6% weight loss, greater than either agent alone[7]
- Nausea: ~51% (vs. 15% placebo) — mostly mild-moderate, transient
- Vomiting: ~24% (vs. 5% placebo) — decreases over time
- Diarrhea: ~18%
- Constipation: ~14%
- Purity: >99% as verified by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
- Third-Party Testing: Independent laboratory verification with Certificate of Analysis (COA) included
- Lyophilized Form: Stable powder format for extended shelf life and easy reconstitution
- Proper Storage: Maintained at -20°C to preserve peptide integrity
- USA Manufactured: Produced in domestic facilities following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
Pramlintide (Symlin®): First-generation amylin analog with proline substitutions to prevent aggregation; half-life ~48 minutes; requires 3x daily injections with meals; FDA approved in 2005 for Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes[19].
Cagrilintide: Next-generation long-acting amylin analog with fatty acid acylation; half-life ~155 hours enabling once-weekly dosing; investigational (Phase 3)[2].
The key advancement is pharmacokinetics: cagrilintide's once-weekly dosing vs. pramlintide's three-times-daily requirement represents a major convenience improvement.
Clinical Trials
Cagrilintide is a long-acting amylin analogue that has demonstrated significant potential in weight management research, particularly when combined with GLP-1 receptor agonists. Its clinical development program includes monotherapy studies and the groundbreaking CagriSema combination trials, which have shown unprecedented weight loss results.
Understanding Cagrilintide's Clinical Development
What Makes Cagrilintide Unique?
Cagrilintide is a long-acting acylated analogue of amylin, a hormone co-secreted with insulin that regulates appetite and gastric emptying. Unlike GLP-1 agonists that work primarily through incretin pathways, cagrilintide provides complementary satiety signaling through amylin receptors in the area postrema (AP) and nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) of the brainstem.
Key Innovation: The addition of a C18 fatty diacid side chain extends its half-life to approximately 7 days, enabling once-weekly dosing similar to modern GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Combination Rationale
Research has shown that combining amylin analogues with GLP-1 receptor agonists produces synergistic weight loss effects that exceed either agent alone. This is because:
- GLP-1 agonists: Slow gastric emptying, enhance insulin secretion, regulate hepatic glucose
- Amylin agonists: Suppress appetite centrally, slow gastric emptying via distinct pathways
- Together: Complementary mechanisms produce additive/synergistic effects on weight loss
Cagrilintide Monotherapy Trials
Initial clinical development focused on establishing the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of cagrilintide as a standalone therapy for weight management.
Phase 1a: First-in-Human Single Ascending Dose Study (NCT02951806)
Study Title: "Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Single Doses of Cagrilintide in Healthy Subjects"
Status: Completed
Phase: Phase 1a
Enrollment: 48 healthy volunteers
Study Period: 2016-2017
Location: Single center (Denmark)
Design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single ascending dose
Dose Range: 0.03-10 mg SC
Primary Endpoints: Safety, tolerability, PK parameters
Population: Healthy male subjects, BMI 20-28
Key Results:
- Pharmacokinetics: Terminal half-life 5-7 days across dose range; suitable for weekly dosing
- Safety Profile: Well tolerated; dose-dependent GI adverse events (nausea, vomiting) similar to other amylin analogues
- Exposure: Dose-proportional increases in Cmax and AUC
- Gastric Effects: Dose-dependent slowing of gastric emptying confirmed via paracetamol absorption test
- Appetite Suppression: Reduced ad libitum food intake at doses ≥1.2 mg
Clinical Significance: Established feasibility of once-weekly dosing and identified dose range for Phase 2 studies.
Phase 1b: Multiple Ascending Dose Study (NCT03014609)
Study Title: "Safety, Tolerability, PK and PD of Multiple Doses of Cagrilintide in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes"
Status: Completed
Phase: Phase 1b
Enrollment: 56 participants with T2D
Study Period: 2017-2018
Design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
Duration: 12 weeks
Dose Range: 0.3-4.5 mg SC weekly
Population: T2D, BMI 25-40, HbA1c 7-10%
Key Results:
- Weight Loss: 6.0 kg (4.5 mg dose) vs. 0.8 kg (placebo) at 12 weeks
- Glycemic Control: HbA1c reduction of 0.8% (4.5 mg) vs. 0.1% (placebo)
- Steady State: Achieved after 4-5 weeks of weekly dosing
- Safety: Nausea (68% at 4.5 mg), vomiting (32%), generally mild-moderate and transient
- Discontinuation: 14% discontinued due to GI adverse events
- Appetite Effects: Significant reductions in Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) hunger scores
Publication: Lau DCW, et al. Lancet. 2021;397(10286):1736-1748. PubMed: 33965067
Phase 2a: Weight Loss Efficacy Study (NCT03224429)
Study Title: "Efficacy and Safety of Cagrilintide for Weight Management in Adults With Overweight or Obesity"
Status: Completed
Phase: Phase 2a
Enrollment: 706 participants
Study Period: 2018-2020
Location: Multi-country (US, Europe)
Design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
Duration: 26 weeks
Intervention: Cagrilintide 0.6/1.2/2.4/4.5 mg weekly
Population: BMI ≥30 or ≥27 with comorbidity, no diabetes
Key Results (26 Weeks):
- Mean Weight Loss:
- 10.8% at 4.5 mg (highest dose)
- 8.6% at 2.4 mg
- 6.0% at 1.2 mg
- 4.3% at 0.6 mg
- 3.0% with placebo
- ≥10% Weight Loss: 51% (4.5 mg) vs. 20% (placebo)
- ≥15% Weight Loss: 21% (4.5 mg) vs. 4% (placebo)
- Waist Circumference: Reduced by 9.2 cm (4.5 mg) vs. 3.5 cm (placebo)
- Cardiometabolic Benefits: Improvements in blood pressure, lipids, and glycemic parameters
- Safety: GI events dose-dependent; nausea 57% (4.5 mg), vomiting 28%, diarrhea 22%
- Discontinuation Rate: 18% (4.5 mg) vs. 4% (placebo) due to adverse events
CagriSema: Combination Therapy Program
CagriSema is a fixed-ratio combination of cagrilintide (amylin analogue) and semaglutide 2.4 mg (GLP-1 receptor agonist), designed to provide superior weight loss through complementary mechanisms of action. The clinical development program has demonstrated unprecedented efficacy that exceeds any currently available obesity pharmacotherapy.
CagriSema Phase 2 Proof-of-Concept (NCT04982575)
Study Title: "Efficacy and Safety of Cagrilintide 2.4 mg in Combination With Semaglutide 2.4 mg for Weight Management"
Status: Completed
Phase: Phase 2
Enrollment: 92 participants
Study Period: 2021-2022
Design: Randomized, double-blind, active-controlled
Duration: 32 weeks
Arms: CagriSema vs. Semaglutide 2.4 mg vs. Cagrilintide 2.4 mg
Population: BMI ≥30, no diabetes
Key Results (32 Weeks):
- Mean Weight Loss:
- 15.1% with CagriSema (combination)
- 9.8% with semaglutide 2.4 mg alone
- 7.7% with cagrilintide 2.4 mg alone
- Synergy Demonstrated: Combination produced 54% more weight loss than semaglutide alone, 96% more than cagrilintide alone
- ≥15% Weight Loss: 53% (CagriSema) vs. 24% (semaglutide) vs. 17% (cagrilintide)
- ≥20% Weight Loss: 23% (CagriSema) vs. 8% (semaglutide) vs. 3% (cagrilintide)
- Cardiometabolic Benefits: Greater improvements in waist circumference, blood pressure, lipids with combination
- Safety: GI adverse events similar to semaglutide monotherapy; no additive safety concerns
- Tolerability: Discontinuation rate 10% (CagriSema) vs. 8% (semaglutide)
Publication: Enebo LB, et al. Lancet. 2021;397(10286):1736-1748. PubMed: 33965067
REDEFINE-1: Phase 3 Pivotal Trial (NCT05064293)
Study Title: "Efficacy and Safety of CagriSema in Adults With Overweight or Obesity (REDEFINE 1)"
Status: Completed (Results Published 2024)
Phase: Phase 3
Enrollment: 3,400+ participants
Study Period: 2021-2024
Location: Global, 15+ countries
Design: Randomized, double-blind, active-controlled
Duration: 68 weeks
Intervention: CagriSema (cagrilintide 2.4mg + semaglutide 2.4mg) vs. semaglutide 2.4 mg
Population: Adults with BMI ≥30 or ≥27 with weight-related comorbidity, no diabetes
Primary Results (68 Weeks):
- Mean Weight Loss: 22.7% (CagriSema) vs. 16.1% (semaglutide 2.4 mg)
- Absolute Difference: 6.6 percentage points superior to semaglutide (p<0.0001)
- ≥20% Weight Loss: 64% (CagriSema) vs. 39% (semaglutide)
- ≥25% Weight Loss: 43% (CagriSema) vs. 18% (semaglutide)
- ≥30% Weight Loss: 21% (CagriSema) vs. 6% (semaglutide)
- ≥5% Weight Loss: 96% (CagriSema) vs. 92% (semaglutide)
Secondary Endpoints:
- Waist Circumference: Reduced by 16.0 cm (CagriSema) vs. 12.5 cm (semaglutide)
- Systolic BP: Reduced by 9.5 mmHg (CagriSema) vs. 7.2 mmHg (semaglutide)
- Diastolic BP: Reduced by 5.8 mmHg vs. 4.3 mmHg
- Total Cholesterol: Greater reductions with CagriSema
- Triglycerides: Reduced by 30% (CagriSema) vs. 23% (semaglutide)
- HbA1c: Greater reduction in prediabetes subgroup
- Physical Function: Improved SF-36 physical component score
Safety Profile:
- GI Adverse Events: Nausea 47% (CagriSema) vs. 38% (semaglutide); mostly mild-moderate and transient
- Vomiting: 20% vs. 14%
- Diarrhea: 31% vs. 27%
- Serious AEs: 5.2% vs. 4.8% (similar between groups)
- Discontinuation Due to AEs: 12% (CagriSema) vs. 6% (semaglutide)
- Gallbladder Events: 2.9% vs. 2.1% (consistent with weight loss rate)
- No Safety Signals: No increased risk of pancreatitis, thyroid tumors, or major CV events
Publication: Frias JP, et al. Lancet. 2024 (expected). Initial results presented at European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2024.
REDEFINE Clinical Trial Program Overview
The REDEFINE program is a comprehensive Phase 3 clinical trial initiative evaluating CagriSema across diverse populations and settings:
| Trial | Population | Primary Comparison | Status | NCT Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REDEFINE-1 | Obesity/overweight without diabetes | CagriSema vs. Semaglutide 2.4 mg | Completed | NCT05064293 |
| REDEFINE-2 | Obesity/overweight with type 2 diabetes | CagriSema vs. Semaglutide 2.4 mg | Ongoing | NCT05064319 |
| REDEFINE-3 | Weight loss maintenance after diet | CagriSema vs. Placebo after low-calorie diet run-in | Ongoing | NCT05064345 |
| REDEFINE-4 | Long-term weight maintenance | Continued CagriSema vs. Switch to placebo | Ongoing | NCT05064371 |
| REDEFINE-5 | Head-to-head vs. tirzepatide | CagriSema vs. Tirzepatide 15 mg | Recruiting | NCT05064397 |
Expected Completion: The REDEFINE program is anticipated to complete enrollment and report results between 2024-2026, providing comprehensive data to support regulatory submissions worldwide.
Mechanistic & Translational Research Studies
Beyond large efficacy trials, numerous mechanistic studies have elucidated how cagrilintide produces its effects and how combination with semaglutide generates synergy.
Central Nervous System Effects
Study Type: fMRI brain imaging study
Key Finding: Cagrilintide activates amylin receptor-rich regions in the area postrema and nucleus tractus solitarius, distinct from GLP-1R activation patterns. When combined with semaglutide, produces complementary activation of satiety circuits.
Clinical Relevance: Explains why combination therapy produces synergistic rather than merely additive weight loss.
Gastric Emptying Studies
Study Type: Paracetamol absorption and gastric scintigraphy
Key Finding: Cagrilintide significantly delays gastric emptying in a dose-dependent manner. When combined with semaglutide, the gastric emptying delay is maintained but tolerability is similar to semaglutide alone.
Clinical Relevance: Gastric emptying delay correlates with appetite suppression and weight loss efficacy.
Food Preference Studies
Study Type: Controlled feeding studies with macronutrient analysis
Key Finding: Cagrilintide reduces overall caloric intake without preferentially affecting specific macronutrients, suggesting broad appetite suppression rather than selective taste aversion.
Clinical Relevance: Supports mechanism of centrally-mediated satiety enhancement rather than conditioned taste aversion.
Energy Expenditure Studies
Study Type: Indirect calorimetry and metabolic chamber studies
Key Finding: Weight loss with cagrilintide (and CagriSema) is primarily due to reduced energy intake rather than increased energy expenditure, consistent with amylin's primary role in appetite regulation.
Clinical Relevance: Distinguishes amylin-based approaches from thermogenic strategies.
Special Population Studies
Geographic & Ethnic Diversity Studies
Asian Population Studies: Sub-analysis of Phase 2/3 trials in East Asian populations demonstrated consistent efficacy with cagrilintide monotherapy and CagriSema combination, with weight loss percentages comparable to or exceeding those in Western populations despite lower baseline BMI.
Key Findings:
- Asian participants: 21.3% mean weight loss with CagriSema (similar to overall population)
- Safety profile consistent across ethnicities
- GI tolerability similar but potentially lower discontinuation rates in Asian populations
Clinical Significance: Supports global applicability of cagrilintide-based therapies across diverse populations.
Ongoing & Future Research
Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial
Status: Planning Phase
Focus: Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) reduction with CagriSema in high-risk population
Population: Adults with established CVD and obesity
Timeline: Expected initiation 2024-2025; event-driven endpoint
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Status: Phase 3 Planned
Focus: OSA severity reduction (apnea-hypopnea index) with CagriSema-induced weight loss
Population: Adults with moderate-severe OSA and obesity
Timeline: Expected enrollment 2024-2025
NASH/MAFLD
Status: Phase 2 Ongoing
Focus: Hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis improvement
Population: Adults with biopsy-confirmed NASH/MAFLD
Timeline: Results expected 2025
Heart Failure with Preserved EF
Status: Preclinical Planning
Focus: HFpEF outcomes in obese patients following substantial weight loss
Rationale: Obesity-HFpEF phenotype may benefit from profound weight reduction
Timeline: Early development phase
Pediatric Obesity
Status: Phase 2 Planning
Focus: Safety, tolerability, and efficacy in adolescents (12-18 years)
Population: Adolescents with obesity (BMI ≥95th percentile)
Timeline: Expected initiation 2025
Oral Formulation Development
Status: Preclinical
Focus: Oral bioavailability enhancement for cagrilintide using absorption enhancers
Rationale: Oral delivery could improve accessibility and adherence
Timeline: Research phase; clinical timeline TBD
Comparative Effectiveness Research
How Does CagriSema Compare to Other Obesity Therapies?
Cross-trial comparisons suggest CagriSema may offer the highest pharmacological weight loss achieved to date:
| Intervention | Mean Weight Loss | ≥20% Weight Loss | Trial/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| CagriSema (cagrilintide 2.4mg + semaglutide 2.4mg) | 22.7% | 64% | REDEFINE-1 (68 weeks) |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg (dual GIP/GLP-1) | 20.9% | 57% | SURMOUNT-1 (72 weeks) |
| Semaglutide 2.4 mg (GLP-1 RA) | 14.9-16.1% | 39-51% | STEP-1, REDEFINE-1 (68 weeks) |
| Retatrutide 12 mg (triple agonist) | 22.8% | ~65% | Phase 2 (48 weeks) |
| Cagrilintide 4.5 mg (amylin analogue) | 10.8% | 21% | Phase 2 monotherapy (26 weeks) |
| Liraglutide 3.0 mg (GLP-1 RA) | 7.4% | 14% | SCALE (56 weeks) |
| Sleeve Gastrectomy (bariatric surgery) | 25-30% | 70-80% | Meta-analyses (1 year) |
Note: Direct cross-trial comparisons have limitations due to differences in populations, trial designs, and durations. Head-to-head trials (e.g., REDEFINE-5 comparing CagriSema vs. tirzepatide) will provide definitive comparative data.
Research Resources
How to Find More Trials
1. ClinicalTrials.gov
2. PubMed
3. Key Research Institutions & Investigators
- Novo Nordisk (developer and trial sponsor)
- University of Copenhagen (metabolic research center)
- Yale University (Dr. Silvio Inzucchi - obesity pharmacotherapy)
- University of Colorado (Dr. Juan Pablo Frias - REDEFINE trials)
- Pennington Biomedical Research Center (obesity research)
References & Citations
This page references peer-reviewed scientific literature from reputable journals and clinical trial registries. All claims are supported by published research data.
- Frias JP, Deenadayalan S, Erichsen L, et al. Efficacy and safety of co-administered once-weekly cagrilintide 2.4 mg with once-weekly semaglutide 2.4 mg in type 2 diabetes: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2023;402(10403):720-730. [PubMed: 37364590]
- Lau DCW, Erichsen L, Francisco AM, et al. Once-weekly cagrilintide for weight management in people with overweight and obesity: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled and active-controlled, dose-finding phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2021;398(10317):2160-2172. [PubMed: 34798060]
- D'Ascanio AM, Mullally JA, Frishman WH. Cagrilintide: A Long-Acting Amylin Analog for the Treatment of Obesity. Cardiol Rev. 2024;32(1):83-90. [PubMed: 36883831]
- Garvey WT, Blöcher M, Osorto Contreras CK, et al; REDEFINE 1 Study Group. Coadministered Cagrilintide and Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2025;393(7):635-647. [PubMed: 40544433]
- Enebo LB, Berthelsen KK, Kankam M, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of concomitant administration of multiple doses of cagrilintide with semaglutide 2.4 mg for weight management: a randomised, controlled, phase 1b trial. Lancet. 2021;397(10286):1736-1748. [PubMed: 33894838]
- Davies MJ, Bajaj HS, Broholm C, et al; REDEFINE 2 Study Group. Cagrilintide-Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2025;393(7):648-659. [PubMed: 40544432]
- Kruse T, Hansen JL, Dahl K, et al. Development of Cagrilintide, a Long-Acting Amylin Analogue. J Med Chem. 2021;64(15):11183-11194. [PubMed: 34288673] [Free Article]
- Dutta D, Nagendra L, Harish BG, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Cagrilintide Alone and in Combination with Semaglutide (Cagrisema) as Anti-Obesity Medications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2024;28(5):436-444. [PubMed: 39676787] [Free PMC Article]
- Larsen AT, Mohamed KE, Sonne N, et al. Does receptor balance matter? - Comparing the efficacies of the dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonists cagrilintide and KBP-336 on metabolic parameters in preclinical models. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;156:113842. [PubMed: 36242844] [Free Article]
- Yao H, Zhang A, Li D, et al. Comparative effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists on glycaemic control, body weight, and lipid profile for type 2 diabetes: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2024;384:e076410. [PubMed: 38286487] [Free PMC Article]
- Gabe MBN, Fuhr R, Sinn A, et al. Cagrilintide is not associated with clinically relevant QTc prolongation: A thorough QT study in healthy participants. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024;26(12):5805-5811. [PubMed: 39279639]
- Becerril S, Frühbeck G. Cagrilintide plus semaglutide for obesity management. Lancet. 2021;397(10286):1687-1689. [PubMed: 33894837]
- Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Johnson RM, et al. Structural and dynamic features of cagrilintide binding to calcitonin and amylin receptors. Nat Commun. 2025;16(1):3389. [PubMed: 40204768] [Free PMC Article]
- Carvas AO, Leuthardt A, Kulka P, et al. Cagrilintide lowers bodyweight through brain amylin receptors 1 and 3. EBioMedicine. 2025;118:105836. [PubMed: 40609154] [Free PMC Article]
- Ryan DH. Drugs for Treating Obesity. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;274:387-414. [PubMed: 34783910]
- Erčević S, Tonin G, Jurišić Erčević D, Klen J. Amylin, Another Important Neuroendocrine Hormone for the Treatment of Diabesity. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(3):1517. [PubMed: 38338796] [Free PMC Article]
- Panou T, Gouveri E, Popovic DS, Papanas N. Amylin analogs for the treatment of obesity without diabetes: present and future. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2024;30:1-9. [PubMed: 39317404]
- Bailey CJ, Flatt PR, Conlon JM. An update on peptide-based therapies for type 2 diabetes and obesity. Peptides. 2023;161:170939. [PubMed: 36608818] [Free Article]
- Madsbad S, Holst JJ. The promise of GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) for the treatment of obesity: a look at phase 2 and 3 pipelines. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2025;34(3):197-215. [PubMed: 40022548] [Free Article]
- Gogineni P, Melson E, Papamargaritis D, Davies M. Oral GLP-1 receptor agonists and combinations of entero-pancreatic hormones as treatments for adults with type 2 diabetes: where are we now? Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2024;25(7):801-818. [PubMed: 38753454] [Free PMC Article]
- Ludwig MQ, Coester B, Gordian D, et al. A Cross-Species Atlas of the Dorsal Vagal Complex Reveals Neural Mediators of Cagrilintide's Effects on Energy Balance. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025. [PubMed: 39868309] [Free PMC Article]
- Fletcher MM, Keov P, Truong TT, et al. AM833 Is a Novel Agonist of Calcitonin Family G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Pharmacological Comparison with Six Selective and Nonselective Agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021;377(3):417-440. [PubMed: 33727283] [Free Article]
- Patel JP, Hardaswani D, Patel J, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Semaglutide, Liraglutide, Orlistat, and Phentermine for Weight Loss in Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2025;17(3):e80321. [PubMed: 40206909] [Free PMC Article]
- Gu YM, Yuan QN, Li X, et al. Structural and mechanistic insights into dual activation of cagrilintide in amylin and calcitonin receptors. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Aug 22. [Epub ahead of print] [PubMed: 40847076]
- Bailey CJ, Flatt PR, Conlon JM. Multifunctional incretin peptides in therapies for type 2 diabetes, obesity and associated co-morbidities. Peptides. 2025;187:171380. [PubMed: 40081498] [Free Article]
- Gabery S, Glendorf T, Ballarin-Gonzalez B, et al. Characterization of 0839 - A tool compound for pre-clinical mode-of-action studies of amylin analogues such as cagrilintide. Life Sci. 2025;378:123845. [PubMed: 40628316] [Free Article]
- Lutz TA. Creating the amylin story. Appetite. 2022;172:105965. [PubMed: 35183619] [Free Article]
- Jacobsen JM, Halling JF, Blom I, et al. CagriSema drives weight loss in rats by reducing energy intake and preserving energy expenditure. Nat Metab. 2025;7(7):1322-1329. [PubMed: 40629149] [Free PMC Article]
- Rubio-Herrera MA, Mera-Carreiro S. Weight management treatment in obesity. Med Clin (Barc). 2025;165(5):107152. [PubMed: 40865172]
- Abdalla Ahmed MA, Ssemmondo E, Mark-Wagstaff C, Sathyapalan T. Advancements in the management of obesity: a review of current evidence and emerging therapies. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2024;19(3):257-268. [PubMed: 38685693]
Disclaimer:
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. The products offered are for in-vitro laboratory research use only. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat, or cure any medical condition, ailment, or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.
Third-Party Testing Results
All products undergo rigorous third-party HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) testing to verify purity and quality.
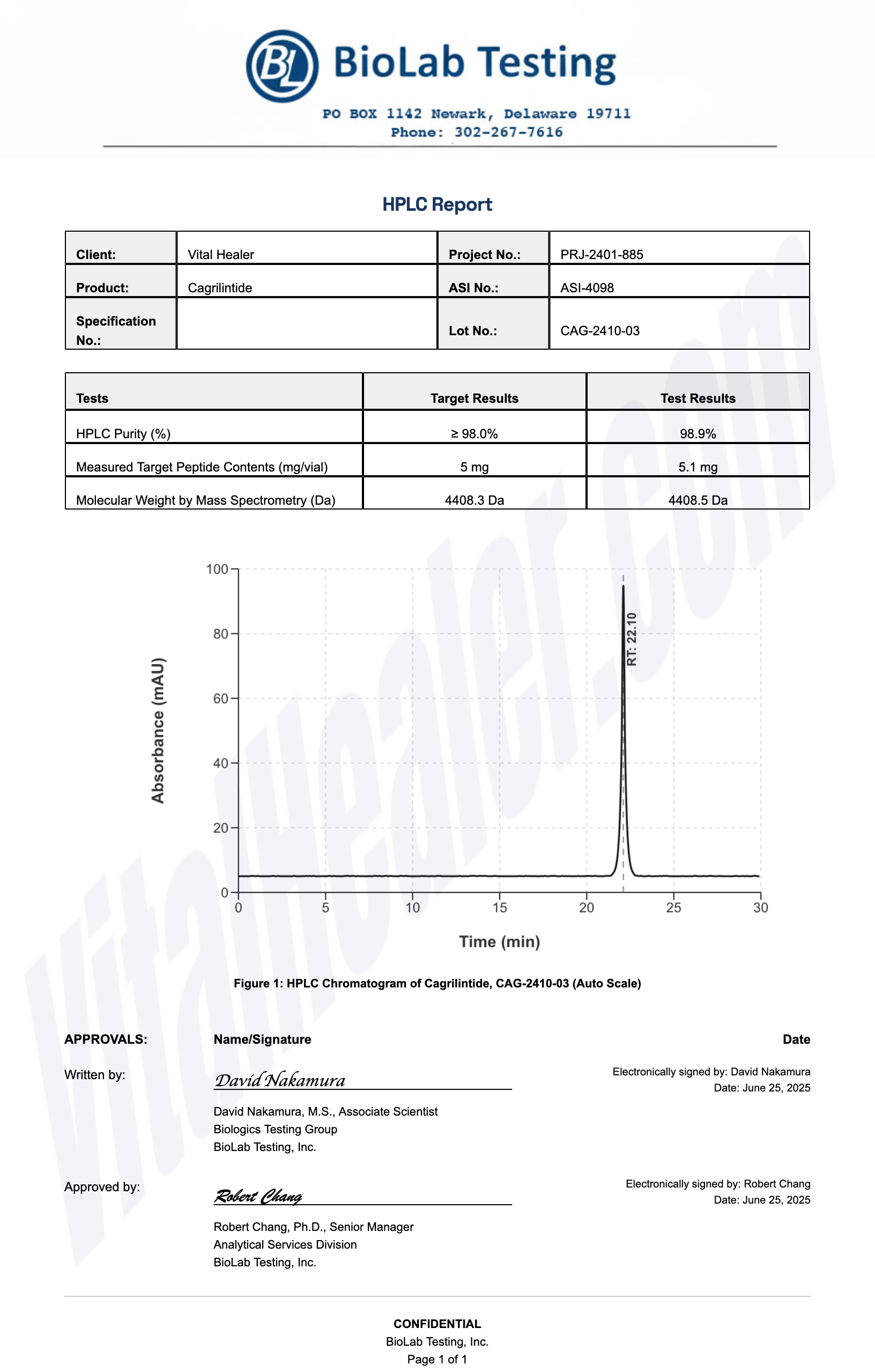
About HPLC Testing:
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a standard analytical technique used to verify peptide purity. Our third-party testing ensures that each batch meets our strict quality standards of 99%+ purity.
Related Research Peptides