Livagen
Livagen, a tetrapeptide bioregulator that modulates chromatin structure, supports hepatic function, and promotes DNA repair.
Key Research Properties:
| SKU: | livagen |
|---|---|
| Purity: | >99% (HPLC Verified) |
| Form: | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C |
| CAS Number: | 62568-57-4 |
| Lot Number: | LIV-2410-12: 20mg |
All products are sold strictly for laboratory and research purposes. Products are not intended for human use or consumption of any kind.
The statements presented on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or disease.
What is Livagen?
Livagen (Lys-Glu-Asp-Ala) is a synthetic tetrapeptide cytogen investigated for its ability to de-heterochromatinize aging lymphocyte chromatin, restore ribosomal gene activity, and support genomic stability in gerontology research models.[1], [2], [3]
Research Themes
- Reactivation of ribosomal genes in senescent lymphocytes.[1], [2]
- Decondensation of pericentromeric and telomeric heterochromatin.[3], [9]
- Correction of genomic instability in cardiovascular aging cohorts.[8], [9]
- Age-dependent modulation of digestive enzyme activity in rats.[4]
- Inhibition of human serum enkephalin-degrading enzymes.[6]
Key Research Findings
- Chromatin Reactivation: Livagen increased nucleolar organizer activity and relaxed densely packed heterochromatin in lymphocytes from individuals aged 72–88 years.[1], [2]
- Genome Architecture: Livagen, alone or with cobalt ions, improved NOR size distribution and acrocentric chromosome associations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy families.[9]
- Genomic Stability: Atherosclerosis patient lymphocytes exhibited reduced chromatin condensation and aneuploidy metrics after Livagen exposure.[8]
- Metabolic Enzymes: Two-week oral administration modulated intestinal and hepatic digestive enzyme activities in an age-dependent manner, restoring senescent profiles toward youthful levels.[4]
- Protein Synthesis Rhythms: Organotypic hepatocyte cultures regained circadian protein synthesis rhythms under Livagen exposure.[5]
- Neuropeptide Metabolism: Livagen inhibited serum enkephalin-degrading enzymes with an IC50 of 20 μM without binding opioid receptors.[6]
Mechanism of Action
Livagen is hypothesized to act through epigenetic modulation of chromatin domains and peptide-processing enzymes rather than via classical receptor agonism.[1], [3], [6]
Chromatin Remodeling
- Promotes de-heterochromatinization of pericentromeric regions in chromosomes 1 and 9 of aged lymphocytes.[1], [2]
- Reactivates ribosomal gene transcription and nucleolar organizer region (NOR) activity.[1], [3]
- Facilitates chromatin decondensation when combined with metal cofactors such as cobalt ions.[8], [9]
Genomic Stability & Stress Adaptation
- Reduces age-associated chromosomal aberrations and aneuploidy indices in lymphocytes from atherosclerosis patients.[8]
- Enhances adaptive response to low-dose gamma irradiation in lymphocytes from elderly donors.[7]
- Modulates NOR associations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy families, suggesting influence on chromosomal pairing and transcription readiness.[9]
Enzymatic & Metabolic Pathways
Research & Evidence
Livagen investigations emphasize chromatin regulation, genomic stability, and metabolic support in aging models.[1]-[9]
Aging Lymphocyte Chromatin
Multiple ex vivo studies cultured lymphocytes from 72–88 year-old donors to evaluate chromatin activation after Livagen exposure.[1], [2], [3]
- Ribosomal gene activation measured via silver staining and NOR counts.
- Assessment of heterochromatin melting parameters and C-segment polymorphism.
- Comparative evaluations against other cytogens such as Epitalon and Vilon.
Cardiometabolic Genomic Studies
Livagen has been combined with cobalt ions to assess genomic integrity in cardiovascular disease cohorts.[8], [9]
- Atherosclerosis patients showed reduced chromatin condensation indices.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy families exhibited increased NOR activity and controlled acrocentric associations.
- Outcomes suggest a role in chromatin decondensation and genomic maintenance during pathologic stress.
Radiation & Stress Adaptation
Elderly donor lymphocytes retained adaptive responses to low-dose gamma irradiation that were enhanced by Livagen pretreatment.[7]
- Evaluated combined exposures to gamma radiation and copper salts.
- Documented improvements in cellular adaptive capacity despite advanced age.
Metabolic & Enzymatic Models
Animal and biochemical studies highlight Livagen’s influence on digestive enzymes and peptide metabolism.[4], [5], [6]
- Age-stratified rats demonstrated bidirectional modulation of enzyme activity.
- Organotypic liver cultures regained circadian protein synthesis rhythms.
- Human serum assays confirmed potent enkephalinase inhibition without opioid receptor engagement.
Dosing & Administration
Published literature does not define clinically validated dosing regimens. Reported experimental approaches include:
- Ex vivo lymphocyte incubation: Peripheral blood lymphocytes from elderly donors were exposed to Livagen for 24–72 hours to analyze chromatin decondensation and NOR activity.[1], [2], [9]
- Oral administration in rodents: Rats received daily Livagen for 14 days to evaluate digestive enzyme activity shifts; dosing concentrations were not disclosed in the abstract.[4]
- Organotypic liver culture exposure: Hepatocyte cultures were treated with Livagen during circadian sampling windows to restore protein synthesis rhythms.[5]
- In vitro serum assays: Human serum samples were incubated with Livagen across micromolar concentrations to determine enkephalinase inhibition kinetics (IC50 = 20 μM).[6]
Safety & Side Effects
Safety observations are limited to laboratory models; comprehensive toxicology, reproductive safety, and pharmacovigilance data are unavailable.[1], [4], [7]
Reported Observations
- No cytotoxic effects were described in cultured lymphocytes during chromatin reactivation studies.[1], [2]
- Livagen normalized genomic instability markers without documented adverse genomic effects in atherosclerosis cohorts.[8]
- Rat studies reported enzyme modulation without noting overt toxicity; however, histological and organ function assessments were not detailed.[4]
- Serum enzyme assays showed potent inhibitory activity without receptor binding, but systemic safety implications remain unknown.[6]
Unresolved Risks
Frequently Asked Questions
Clinical Trials & Research Status
No Livagen-specific interventional trials are registered on ClinicalTrials.gov; the studies below summarize peer-reviewed investigations spanning ex vivo human assays and animal models.
| Study | Type & Model | Protocol Highlights | Primary Outcomes | Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effects of Livagen peptide on chromatin activation in lymphocytes from old people | Ex vivo, human lymphocytes (aged donors) | Peripheral blood lymphocytes from 72–88 year-old individuals cultured with Livagen to assess chromatin melting dynamics. | NOR activation, heterochromatin decondensation, ribosomal gene transcription.[1] | PMID: 12533768 |
| Effects of short peptides on lymphocyte chromatin in senile subjects | Ex vivo, human lymphocytes | Compared Livagen with other cytogens in elderly donor cultures using cytogenetic staining. | Chromatin condensation metrics, ribosomal gene activity.[2] | PMID: 15085253 |
| Activation of pericentromeric and telomeric heterochromatin in cultured lymphocytes from old individuals | Ex vivo, human lymphocytes | Evaluated telomeric and pericentromeric heterochromatin changes with Livagen exposure. | Chromatin activation at telomeric regions, NOR dynamics.[3] | PMID: 17460203 |
| [Effect of peptide Livagen on activity of digestive enzymes in gastrointestinal tract and non-digestive organs in rats of different ages] | In vivo, Wistar rats (young vs. aged) | Daily oral Livagen for 14 days followed by enzyme assays in GI tract, liver, and kidney tissues. | Dipeptidase activity modulation and age-related normalization.[4] | PMID: 16075683 |
| [Rhythm of protein synthesis in cultures of hepatocytes from rats of different ages. Norm and effect of the peptide Livagen] | Organotypic liver culture | Tracked circadian protein synthesis in hepatocytes with and without Livagen supplementation. | Restoration of protein synthesis rhythms in aged hepatocytes.[5] | PMID: 15926314 |
| [Effect of new peptide bioregulators livagen and epitalon on enkephalin-degrading enzymes in human serum] | In vitro, human serum | Measured enkephalinase activity across micromolar Livagen concentrations. | IC50=20 μM for enkephalinase inhibition; no opioid receptor binding.[6] | PMID: 12942748 |
| [Variability of radiation-induced adaptive response in old age individuals and their correction by Peptide bioregulator - Livagen] | Ex vivo, elderly lymphocytes | Preconditioned lymphocytes with Livagen before gamma exposure and copper challenge. | Adaptive response magnitude, genomic damage mitigation.[7] | PMID: 17921545 |
| [Genomic instability in atherosclerosis] | Ex vivo, patient lymphocytes | Examined chromosomal aberrations in atherosclerosis patients treated with Livagen ± cobalt ions. | Genomic instability indices, chromatin condensation markers.[8] | PMID: 25541832 |
| [Effect of peptide bioregulator and cobalt ions on the activity of NORs and associations of acrocentric chromosomes in lymphocytes of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and their relatives] | Ex vivo, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients & relatives | Assessed NOR size classes and acrocentric chromosome associations after Livagen ± cobalt exposure. | NOR grading, acrocentric association frequency, heterochromatin status.[9] | PMID: 25341254 |
References & Scientific Citations
Research Integrity
Citations below link directly to source journals or PubMed listings for verification.
- Khavinson VKh, Lezhava TA, Monaselidze JG, et al. Effects of Livagen peptide on chromatin activation in lymphocytes from old people. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2002 Oct;134(4):389-392. doi:10.1023/A:1021924702103. PubMed
- Khavinson VKh, Lezhava TA, Malinin VV. Effects of short peptides on lymphocyte chromatin in senile subjects. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2004 Jan;137(1):78-81. doi:10.1023/B:BEBM.0000024393.40560.05. PubMed
- Lezhava T, Jokhadze T. Activation of pericentromeric and telomeric heterochromatin in cultured lymphocytes from old individuals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Apr;1100:387-399. doi:10.1196/annals.1395.043. PubMed
- Timofeeva NM, Khavinson VKh, Malinin VV, Nikitina AA, Egorova VV. [Effect of peptide Livagen on activity of digestive enzymes in gastrointestinal tract and non-digestive organs in rats of different ages]. Adv Gerontol. 2005;16:92-96. PubMed
- Brodskii VIa, Khavinson VKh, Zolotarev IuA, et al. [Rhythm of protein synthesis in cultures of hepatocytes from rats of different ages. Norm and effect of the peptide Livagen]. Izv Akad Nauk Ser Biol. 2001;(5):517-521. PubMed
- Kost NV, Sokolov OIu, Gabaeva MV, et al. [Effect of new peptide bioregulators livagen and epitalon on enkephalin-degrading enzymes in human serum]. Izv Akad Nauk Ser Biol. 2003;(4):427-429. PubMed
- Dzhokhadze TA, Buadze TZh, Dvalishvili NA, Lezhava TA. [Variability of radiation-induced adaptive response in old age individuals and their correction by peptide bioregulator - Livagen]. Georgian Med News. 2007;(148-149):50-54. PubMed
- Dzhokhadze TA, Buadze TZh, Gaiozishvili MN, Kakauridze NG, Lezhava TA. [Genomic instability in atherosclerosis]. Georgian Med News. 2014;(236):82-86. PubMed
- [No authors listed]. [Effect of peptide bioregulator and cobalt ions on the activity of NORs and associations of acrocentric chromosomes in lymphocytes of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and their relatives]. Georgian Med News. 2014;(234):134-137. PubMed
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 87919683, Lys-Glu-Asp-Ala. Updated 12 Feb 2015. Accessed 13 Nov 2025. PubChem
Third-Party Testing Results
All products undergo rigorous third-party HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) testing to verify purity and quality.
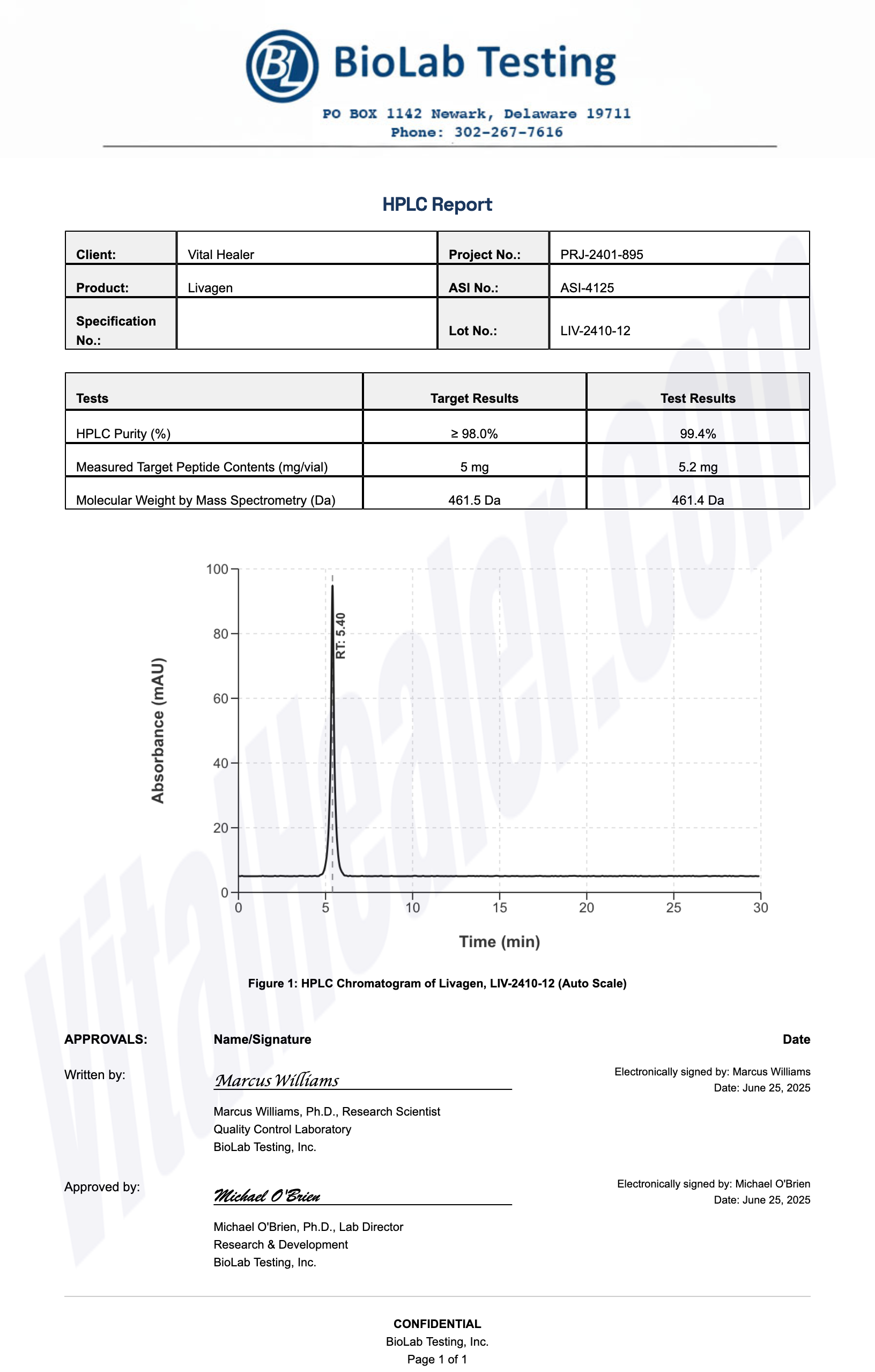
About HPLC Testing:
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a standard analytical technique used to verify peptide purity. Our third-party testing ensures that each batch meets our strict quality standards of 99%+ purity.
Related Research Peptides