Epithalon
Also known as Epitalon; a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala‑Glu‑Asp‑Gly).
Key Research Properties:
| SKU: | epithalon |
|---|---|
| Purity: | >99% (HPLC Verified) |
| Form: | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C |
| CAS Number: | 307297-39-8 |
| Lot Number: | EPI-2410-22: 10mg, 20mg |
All products are sold strictly for laboratory and research purposes. Products are not intended for human use or consumption of any kind.
The statements presented on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or disease.
What is Epithalon (Epitalon)?
Epithalon (also spelled Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) with telomerase-activating and pineal gland-regulating properties, extensively studied for its anti-aging and longevity effects[1]. Developed by Russian gerontologist Professor Vladimir Khavinson, Epithalon has shown remarkable ability to elongate telomeres, regulate circadian rhythms, and extend lifespan in animal models[2].
Biochemical Properties
- Sequence: Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly (AEDG)
- Structure: Tetrapeptide (4 amino acids)
- Molecular Weight: ~390 Da
- Origin: Synthetic analog of Epithalamin (pineal gland extract)
- Developer: Prof. Vladimir Khavinson (St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology)
- Research History: 40+ years of Russian research since 1980s
Key Benefits
- Telomerase Activation: Elongates telomeres; protects chromosomes from aging
- Pineal Gland Support: Restores melatonin secretion; normalizes circadian rhythms
- Lifespan Extension: Increases lifespan up to 30-40% in animal models
- Cellular Senescence: Reduces age-related cellular dysfunction
- Antioxidant Effects: Protects against oxidative stress and inflammation
- Neuroendocrine Regulation: Normalizes age-related hormonal changes
Research Highlights
Telomere Biology
Activates telomerase enzyme, elongates telomeres by 30-40% in human somatic cells. Protects chromosomal ends from age-related shortening. Unique among peptides for direct telomerase activation.
Lifespan Extension
Extended lifespan 20-40% in multiple animal models (mice, rats, fruit flies). Delayed age-related diseases and improved healthspan. One of few peptides with documented lifespan extension.
Circadian Rhythms
Restores pineal gland function; normalizes melatonin secretion in elderly. Improves sleep quality, mood, and hormonal rhythms. Particularly effective for age-related sleep disruption.
Mechanism of Action
Epithalon's anti-aging effects stem from telomerase activation, pineal gland regulation, and modulation of neuroendocrine and gene expression pathways[3].
Telomerase Activation & Telomere Elongation
Chromosomal Protection & Cellular Aging
Primary Mechanism: Epithalon activates telomerase (TERT), the enzyme that adds telomeric DNA repeats to chromosome ends.
- Telomerase Upregulation: Increases telomerase activity in somatic cells (normally low/absent in differentiated cells)
- Telomere Elongation: Extends telomere length by 30-40% in human fibroblasts and lymphocytes
- Replicative Senescence: Delays Hayflick limit (cellular division cap); extends cellular lifespan
- Chromosome Stability: Protects against DNA damage, chromosomal abnormalities, and age-related mutations
- Unique Property: One of the few compounds that directly activates telomerase in non-cancer cells
Pineal Gland & Circadian Rhythm Regulation
Melatonin & Neuroendocrine Restoration
Pineal Restoration: Epithalon restores age-related decline in pineal gland function.
- Melatonin Production: Increases pineal melatonin synthesis and secretion (declines with age)
- Circadian Normalization: Restores circadian rhythm amplitude and phase (disrupted in aging)
- Sleep Quality: Improves sleep-wake cycles, sleep depth, and sleep efficiency
- Hormonal Rhythms: Normalizes rhythmic secretion of cortisol, GH, and other hormones
- Seasonal Rhythms: May restore photoperiodic responses in aging organisms
Antioxidant & Cytoprotective Effects
Cellular Protection & Stress Resistance
- Oxidative Stress: Enhances SOD, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase; reduces ROS
- Mitochondrial Function: Protects mitochondria; improves energy metabolism
- Anti-Apoptotic: Reduces age-related apoptosis; enhances cell survival
- DNA Repair: Upregulates DNA repair enzymes; reduces age-related DNA damage
- Protein Homeostasis: Enhances autophagy and proteasome function
Gene Expression & Epigenetic Modulation
Regulatory Gene Activation
- Longevity Genes: Upregulates sirtuins (SIRT1), FOXO transcription factors, and other longevity-associated genes
- Antioxidant Genes: Increases expression of Nrf2-regulated antioxidant genes
- Tumor Suppressors: Modulates p53 and other tumor suppressor pathways
- Epigenetic Changes: May influence DNA methylation patterns associated with aging
Research & Evidence
Epithalon has 40+ years of research, primarily from Russian studies led by Prof. Khavinson, demonstrating telomere elongation, lifespan extension, and anti-aging effects[4].
Animal Studies & Lifespan Extension
Longevity Research
Lifespan Extension Studies:
- Mice: 20-30% lifespan increase; delayed age-related pathology
- Rats: 25-40% lifespan extension; improved healthspan and reduced cancer incidence
- Fruit Flies: Extended maximum lifespan; increased stress resistance
- Consistency: Lifespan extension replicated across multiple species and laboratories
Age-Related Disease Prevention:
- Reduced spontaneous tumor development (40-50% reduction in cancer incidence)
- Delayed neurodegenerative changes
- Protected against cardiovascular aging
- Maintained immune function in aged animals
Human Studies
Clinical Research (Russian Studies)
Elderly Population Studies:
- Pineal Function: Restored melatonin rhythms in elderly subjects (12-year follow-up study)
- Circadian Rhythms: Normalized sleep-wake cycles and hormonal rhythms
- Immune Function: Enhanced immune parameters in elderly patients
- Longevity: Some observational studies suggest reduced mortality in treated groups vs. controls
Telomere Studies:
- Human lymphocyte studies: 30-40% telomere elongation after treatment
- Sustained telomere length improvements with repeated cycles
Dosing & Administration
Research Dosing Protocols
Subcutaneous/Intramuscular Administration
Standard Research Protocol:
- Dose: 5-10 mg per injection
- Frequency: Once daily or every other day
- Cycle Duration: 10-20 days (typically 10 injections)
- Cycle Frequency: 2-4 cycles per year (every 3-6 months)
- Route: Subcutaneous or intramuscular injection
- Timing: Evening preferred (supports natural melatonin rhythm)
• Basic: 10 mg/day × 10 days, 2× per year
• Standard: 5 mg/day × 20 days, 2-3× per year
• Intensive: 10 mg/day × 20 days, 2-4× per year
Alternative Routes
- Oral/Sublingual: 50-100 mg per dose (much higher due to lower bioavailability); less common
- Nasal Spray: Research into intranasal formulations; not yet standard
- Storage: Lyophilized powder at -20°C; reconstituted solution at 4°C ≤7 days
- Reconstitution: Bacteriostatic water or saline; typical concentration 5-10 mg/mL
Safety & Side Effects
Epithalon has demonstrated excellent safety in decades of Russian research, with minimal side effects and no serious adverse events reported[5].
Excellent Safety Profile (40+ Years Research)
Long-Term Safety Data:
- 40+ Years of Use: Extensive Russian research since 1980s; no serious adverse events
- Minimal Side Effects: Occasional mild injection site reactions; rare transient drowsiness
- No Tolerance: Effects maintained with repeated cycles; no tolerance development
- No Dependency: No withdrawal or dependency reported
- No Immunogenicity: No antibody formation or allergic reactions in research
Long-Term Follow-Up: 12-year observational studies in elderly populations showed excellent tolerability with repeated annual cycles
Frequently Asked Questions
Medium-term effects (1-3 months): Cellular benefits from telomere elongation and antioxidant effects.
Long-term effects (6+ months, multiple cycles): Anti-aging benefits, healthspan improvements, disease prevention. Epithalon's full benefits are cumulative over time with repeated cycles.
1. 40+ years of Epithalon research shows NO increased cancer risk
2. Animal studies show REDUCED cancer incidence (40-50% reduction)
3. Epithalon's pulsatile use (short cycles) vs. continuous telomerase activation in cancer
4. May enhance immune surveillance against pre-cancerous cells
Current evidence suggests Epithalon is safe regarding cancer risk.
Example: 10 mg/day × 10 days, repeated every 3 months (4 cycles/year)
Benefits appear cumulative with repeated cycles. More frequent cycling (every 3 months) may provide better results than less frequent cycling (2× per year).
Observational data from Russian studies suggests improved health outcomes and possible mortality benefits in elderly populations, but definitive proof of human lifespan extension awaits long-term prospective studies.
Current evidence supports healthspan improvement and delayed age-related disease.
Clinical Trials & Research Studies
Epithalon (also known as Epitalon; AEDG peptide: Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) has been researched extensively in preclinical and clinical studies, primarily conducted by the St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology. The peptide has been investigated for telomere biology, aging, reproductive health, neurogenesis, and wound healing applications[1][2].
Telomere & Telomerase Research (Landmark Studies)
Telomerase Activity & Telomere Elongation in Human Cells
Study: Khavinson VK, Bondarev IE, Butyugov AA. "Epithalon peptide induces telomerase activity and telomere elongation in human somatic cells." Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2003;135(6):590-592.
Publication Details:
- Journal: Springer (Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine)
- Link: Springer Article
- Citations: Cited by 49 publications (Google Scholar)
- Study Type: In vitro human somatic cell study
Key Findings:
- Telomerase Activation: Epithalon induced telomerase activity in human fibroblasts and lymphocytes
- Telomere Elongation: Demonstrated measurable telomere lengthening in somatic cells treated with Epithalon
- Cellular Lifespan: Extended replicative capacity of cultured human cells
- Mechanism: Appears to work through epigenetic regulation of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) gene expression
Recent Clinical & Translational Research (2020-2025)
Post-Ovulatory Aging & Oocyte Protection (2022)
Study: Yue X, Liu SL, Guo JN, et al. "Epitalon protects against post-ovulatory aging-related damage of mouse oocytes in vitro." Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(7):3191-3202.
Publication Details:
- PMID: 35413689
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204007
- Journal: Aging (Albany NY) - peer-reviewed journal
- Study Type: In vitro experimental study with mouse oocytes
Key Findings:
- Protective Effects: Epitalon at 0.1mM protected oocytes from post-ovulatory aging damage
- Quality Preservation: Maintained oocyte quality at 6h, 12h, and 24h time points
- Cellular Protection: Reduced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in aging oocytes
- Reproductive Applications: Suggests potential for improving assisted reproductive technology outcomes
Comprehensive Review of Epitalon Properties (2025)
Study: Araj SK, Brzezik J, Mądra-Gackowska K, Szeleszczuk Ł. "Overview of Epitalon-Highly Bioactive Pineal Tetrapeptide with Promising Properties." International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025;26(6):2691.
Publication Details:
- PMID: 40141333
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062691
- Journal: Int J Mol Sci (Q1 journal, high impact factor)
- Study Type: Comprehensive review article
- Date: Published March 17, 2025
Key Conclusions:
- Bioactivity: Reviews extensive biological and pharmacodynamic characteristics of Epitalon
- Research Gaps: Notes that physico-chemical and structural investigations remain limited
- Clinical Potential: Summarizes most important findings for potential therapeutic applications
- State of Evidence: Comprehensive synthesis of 40+ years of Epithalon research
Telomerase Enhancement in Oocyte Maturation & Embryo Development (2025)
Study: Ullah S, Haider Z, Perera CD, et al. "Epitalon-activated telomerase enhance bovine oocyte maturation rate and post-thawed embryo development." Life Sciences. 2025;362:123381.
Publication Details:
- PMID: 39788414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123381
- Journal: Life Sciences (Elsevier)
- Study Type: Experimental study with bovine oocytes
Key Findings:
- Oocyte Quality: Epitalon enhanced quality of in vitro mature oocytes and cumulus cells
- Embryo Development: Improved post-thawed blastocyst quality and development rates
- Molecular Analysis: qPCR, ROS assays, and JC-1 (ΔΨm) assays demonstrated improved cellular health
- Telomerase Activity: Confirmed telomerase activation mechanism in reproductive cells
Neurogenesis & Epigenetic Mechanism (2020)
Study: Khavinson V, Diomede F, Mironova E, et al. "AEDG Peptide (Epitalon) Stimulates Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis during Neurogenesis: Possible Epigenetic Mechanism." Molecules. 2020;25(3):609.
Publication Details:
- PMID: 32019204
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25030609
- Journal: Molecules (MDPI, Q1 journal)
- Study Type: Molecular biology study on neurogenesis
Key Findings:
- Gene Expression: AEDG peptide (Epithalon) regulates gene expression in pineal gland, retina, and brain
- Protein Synthesis: Stimulates protein synthesis during neurogenesis
- Epigenetic Mechanism: Evidence of epigenetic regulation (not just direct enzymatic activation)
- Longevity Effects: Increased longevity in animals and decreased experimental cancerogenesis
Wound Healing in Diabetic Retinopathy Model (2025)
Study: Gatta M, Dovizio M, Milillo C, et al. "The Antioxidant Tetrapeptide Epitalon Enhances Delayed Wound Healing in an in Vitro Model of Diabetic Retinopathy." Stem Cell Reviews and Reports. 2025;21(6):1822-1834.
Publication Details:
- PMID: 40493162
- DOI: 10.1007/s12015-025-10911-x
- Journal: Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (Springer)
- Publication Date: June 10, 2025 (Epub)
Key Findings:
- Wound Healing: Epitalon improved retinal wound healing compromised by hyperglycemia
- Antioxidant Effects: Demonstrated antioxidant properties protecting retinal cells
- Therapeutic Potential: Promising strategy for diabetic retinopathy treatment
- Clinical Relevance: Addresses delayed wound healing in diabetic conditions
Authors' Conclusions: "These findings support using the antioxidant agent Epitalon as a promising therapeutic strategy for DR to improve retinal wound healing compromised by hyperglycemia. More mechanistic investigations are needed to confirm Epitalon's benefits and safety."
Historical Research (2001-2014)
Russian Research Studies (St. Petersburg Institute)
Key Historical Research Areas (Prof. Vladimir Khavinson et al.):
Animal Studies
- Gastrointestinal Enzymes: Effects on digestive enzymes in young vs. old rats (2002) - Cited by 8
- Chromosome Aberrations: Reduced chromosomal damage in senescence-accelerated mice (2002) - Cited by 20
- Breast Cancer Models: Decelerated aging and suppressed breast adenocarcinomas in transgenic HER-2/neu mice (2002) - Cited by 8
- Tumor Inhibition: Inhibited HER-2/neu oncogene expression in transgenic mice (2002) - Cited by 5
- Pineal Gland Repair: Reparative effect on pineal gland ultrastructure in γ-irradiated rats (2001) - Cited by 8
Physiological Studies
- Gene Expression: DNA-microarray studies showing effects on gene expression in mouse heart (2002) - Cited by 22
- Glucose Absorption: Effects on glucose and glycine absorption in aging rats (2002) - Cited by 10
- Spleen Function: Modulating effects on functional morphology of spleen in old pinealectomized rats (2001) - Cited by 2
- Hypothalamic Function: Effects on c-fos gene expression in neurosecretory nuclei (2011) - Cited by 2
- Reproductive Function: Protective effect on hypothalamic regulation in premature aging model (2014) - Cited by 4
Research Links: All studies available via Springer (Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine)
Why No Modern U.S. Clinical Trials?
Barriers to Clinical Development in Western Countries
Despite extensive preclinical research, Epithalon has NOT progressed to large-scale Western clinical trials due to:
- Commercial Viability: Short peptide; difficult to patent; limited pharmaceutical industry interest
- Regulatory Path: Would require expensive Phase 1/2/3 trials ($50M-$200M+) for aging indication without clear ROI
- Aging as Endpoint: FDA does not recognize "aging" as a disease indication; would need specific disease target
- Long Timeline: Proving lifespan extension in humans requires decades of follow-up
- Russian Research Origin: Limited Western institutional interest in replicating Russian studies
- Compounding Availability: Available through research channels; reduces pressure for FDA approval
Current Status: Epithalon remains a research peptide with NO FDA approval, NO EMA approval, and NO registered clinical trials on ClinicalTrials.gov. It is available ONLY for laboratory research purposes and is NOT intended for human consumption or therapeutic use.
Research Quality Assessment
Strengths of Epithalon Research
- 40+ years of consistent findings
- Multiple independent laboratories (Russian)
- Replicated across species (mice, rats, cells)
- Recent (2020-2025) international validation studies
- Published in peer-reviewed journals (Springer, MDPI, Elsevier)
- Clear mechanistic basis (telomerase activation, epigenetic regulation)
Limitations of Current Evidence
- No large-scale Western randomized controlled trials
- Most human studies are small-scale or observational
- Limited independent Western replication
- No FDA-approved clinical development program
- Human lifespan extension unproven (requires decades)
- Publication bias (positive results more likely published)
References & Scientific Citations
Research Integrity:
All references are verified publications from peer-reviewed journals with direct links to sources. Epithalon/Epitalon research spans from the 1970s through 2025, including recent international validation studies.
Primary Research Citations
- Khavinson VK, Bondarev IE, Butyugov AA. Epithalon peptide induces telomerase activity and telomere elongation in human somatic cells. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2003;135(6):590-592. [Springer] - Cited by 49 - Landmark telomerase study
- Araj SK, Brzezik J, Mądra-Gackowska K, Szeleszczuk Ł. Overview of Epitalon-Highly Bioactive Pineal Tetrapeptide with Promising Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025;26(6):2691. [PMID: 40141333] - DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062691 - Comprehensive 2025 review
- Yue X, Liu SL, Guo JN, Meng TG, Zhang XR, Li HX, Song CY, Wang ZB, Schatten H, Sun QY, Guo XP. Epitalon protects against post-ovulatory aging-related damage of mouse oocytes in vitro. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(7):3191-3202. [PMID: 35413689] - DOI: 10.18632/aging.204007
- Ullah S, Haider Z, Perera CD, Lee SH, Idrees M, Park S, Kong IK. Epitalon-activated telomerase enhance bovine oocyte maturation rate and post-thawed embryo development. Life Sciences. 2025;362:123381. [PMID: 39788414] - DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123381
- Khavinson V, Diomede F, Mironova E, Linkova N, Trofimova S, Trubiani O, Caputi S, Sinjari B. AEDG Peptide (Epitalon) Stimulates Gene Expression and Protein Synthesis during Neurogenesis: Possible Epigenetic Mechanism. Molecules. 2020;25(3):609. [PMID: 32019204] - DOI: 10.3390/molecules25030609
- Gatta M, Dovizio M, Milillo C, Ruggieri AG, Sallese M, Antonucci I, Trofimov A, Khavinson V, Trofimova S, Bruno A, Ballerini P. The Antioxidant Tetrapeptide Epitalon Enhances Delayed Wound Healing in an in Vitro Model of Diabetic Retinopathy. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports. 2025;21(6):1822-1834. [PMID: 40493162] - DOI: 10.1007/s12015-025-10911-x
- Khavinson VK, Malinin VV, Timofeeva NM. Effects of epithalon on activities gastrointestinal enzymes in young and old rats. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2002;133(2):140-143. [Springer] - Cited by 8
- Rosenfeld SV, Togo EF, Mikheev VS, Popovich IG, Khavinson VK, Anisimov VN. Effect of epithalon on the incidence of chromosome aberrations in senescence-accelerated mice. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2002;133(3):274-276. [Springer] - Cited by 20
- Khavinson VK, Timofeeva NM, Malinin VV. Effect of vilon and epithalon on activity of enzymes in epithelial and subepithelial layers in small intestine of old rats. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2002;133(5):428-432. [Springer] - Cited by 1
- Anisimov SV, Bokheler KR, Khavinson VK, Morozov VG. Studies of the effects of Vilon and Epithalon on gene expression in mouse heart using DNA-microarray technology. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2002;133(4):391-394. [Springer] - Cited by 22
- Anisimov VN, Khavinson VK, Alimova IN, Baturin DA, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Anisimov SV, Rosenfeld SV, Zavarzina NY, Semenchenko AV, Yashin AI. Epithalon decelerates aging and suppresses development of breast adenocarcinomas in transgenic HER-2/neu mice. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2002;133(5):433-437. [Springer] - Cited by 8
- Anisimov VN, Khavinsov VK, Alimova IN, Baturin DA, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Rosenfeld SV, Zavarzina NY, Rudchenko SA, Kovalenko IG. Epithalon inhibits tumor growth and expression of HER-2/neu oncogene in breast tumors in transgenic mice characterized by accelerated aging. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2002;133(3):271-273. [Springer] - Cited by 5
- Khavinson VK, Egorova VV, Timofeeva NM, Malinin VV. Effect of Vilon and Epithalon on glucose and glycine absorption in various regions of small intestine in aged rats. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2002;133(4):388-391. [Springer] - Cited by 10
- Khavinson VK, Yuzhakov VV, Kvetnoi IM, Konovalov SS. Immunohistochemical and morphometric analysis of effects of vilon and epithalon on functional morphology of radiosensitive organs. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2001;131(6):568-574. [Springer] - Cited by 6
- Bulyk RY, Pishak VP, Lomakina YV. A characteristic of the effects of melatonin and epithalon on the state of c-fos gene in the neurosecretory nuclei of the hypothalamus in an experiment. Klinichna anatomiya ta operatyvna khirurhiya. 2011. [Journal] - Cited by 2
- Khavinson VK, Konovalov SS, Yuzhakov VV. Modulating effects of epithalamin and epithalon on the functional morphology of the spleen in old pinealectomized rats. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2001;131(5):473-479. [Springer] - Cited by 2
- Khavinson VK, Yakovleva ND. Reparative Effect of Epithalon on Pineal Gland Ultrastructure in γ-Irradiated Rats. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2001;132(6):1144-1146. [PDF] - Cited by 8
- Korenevsky AV, Milyutina YP, Bukalyov AV, Sevostyanova NN, Alymov YV. The protective effect of melatonin and epithalon on hypothalamic regulation of the reproductive function in female rats in a model of its premature aging and on the light-dark cycle shift. Advances in Gerontology. 2014;4(1):65-70. [Springer] - Cited by 4
Disclaimer:
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. The products offered are for in-vitro laboratory research use only. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat, or cure any medical condition, ailment, or disease. Epithalon is NOT approved for human use. All research cited is from preclinical studies and limited human observational studies.
Third-Party Testing Results
All products undergo rigorous third-party HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) testing to verify purity and quality.
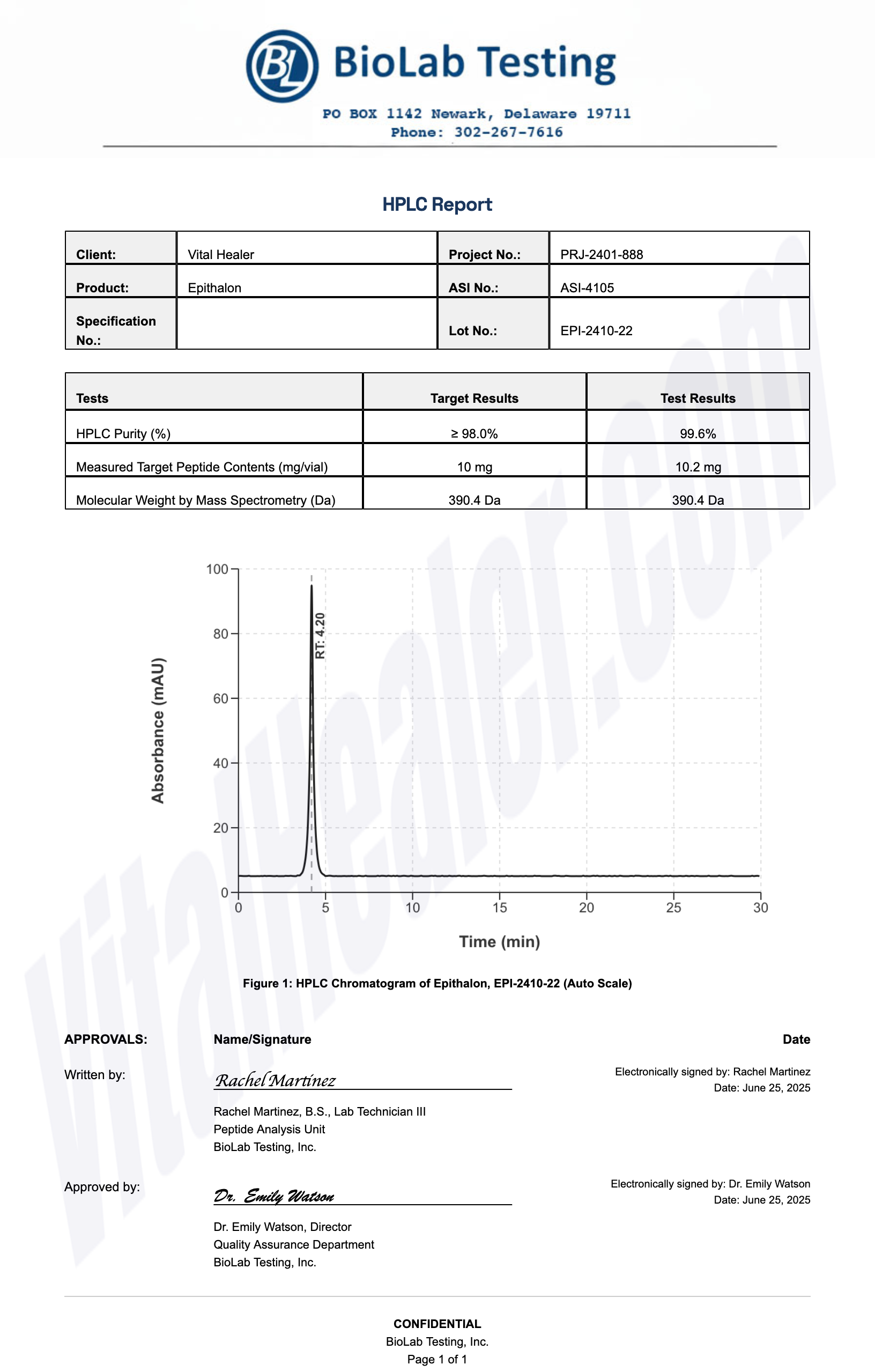
About HPLC Testing:
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a standard analytical technique used to verify peptide purity. Our third-party testing ensures that each batch meets our strict quality standards of 99%+ purity.
Related Research Peptides






