FOXO4-DRI
A designer peptide that interferes with FOXO4–p53 interactions, explored as a senolytic strategy.
Key Research Properties:
| SKU: | foxo4-dri |
|---|---|
| Purity: | >99% (HPLC Verified) |
| Form: | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C |
| CAS Number: | 2460055-10-9 |
| Lot Number: | FOX-2410-02: 10mg |
All products are sold strictly for laboratory and research purposes. Products are not intended for human use or consumption of any kind.
The statements presented on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The products of this company are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition or disease.
What is FOXO4-DRI?
FOXO4-DRI (FOXO4 D-Retro-Inverso) is a novel senolytic peptide that selectively induces apoptosis in senescent cells by disrupting the FOXO4-p53 interaction[1]. Developed by Peter de Keizer's lab at Erasmus University, FOXO4-DRI represents a breakthrough approach to eliminating senescent cells, which accumulate with age and drive age-related diseases[2].
Biochemical Properties
- Structure: D-Retro-Inverso peptide (D-amino acids in reverse sequence)
- Target: FOXO4-p53 protein-protein interaction
- Size: ~30 amino acids
- Developer: Peter de Keizer lab (Erasmus University)
- Publication: 2017 Cell paper (landmark senolytic study)
- Mechanism: Competitive inhibition of FOXO4-p53 binding
Primary Benefits
- Senescent Cell Clearance: Selectively eliminates senescent cells
- Tissue Rejuvenation: Restores function in aged tissues (animal models)
- Hair Regrowth: Restores fur in aged mice (dramatic visual effect)
- Kidney Function: Improves renal function in aged animals
- Physical Performance: Enhances exercise capacity in aged mice
- Chemotherapy Recovery: Accelerates recovery from chemotherapy-induced damage
Key Research Findings
Breakthrough Discoveries
- Selective Senolysis: Induces apoptosis in senescent cells while sparing healthy cells
- Aged Mouse Rejuvenation: Restored fur, kidney function, exercise capacity in naturally aged mice
- Chemotherapy Model: Accelerated recovery from chemotherapy-induced senescence
- FOXO4-p53 Axis: Identified FOXO4-p53 interaction as key senescent cell survival mechanism
- Tissue-Specific Effects: Benefits observed in kidney, liver, muscle, skin
- Safety: No apparent toxicity to healthy cells in preclinical studies
Mechanism of Action
FOXO4-DRI works by disrupting the FOXO4-p53 protein interaction that keeps senescent cells alive, releasing p53 to trigger apoptosis selectively in senescent cells[3].
FOXO4-p53 Interaction Disruption
Senescent Cell Survival Mechanism
Background: In senescent cells, FOXO4 binds to p53 and sequesters it away from the nucleus, preventing p53-mediated apoptosis. This keeps senescent cells alive despite DNA damage.
- FOXO4 Binding: FOXO4-DRI competitively binds to p53, displacing endogenous FOXO4
- p53 Liberation: Free p53 translocates to nucleus and activates pro-apoptotic genes
- Selective Apoptosis: Senescent cells (high p53, high FOXO4) undergo apoptosis
- Healthy Cell Sparing: Normal cells (low FOXO4-p53 interaction) are unaffected
- Specificity: Selectivity based on elevated FOXO4-p53 in senescent cells
Senescent Cell Apoptosis
Programmed Cell Death Induction
- p53 Activation: Liberated p53 activates transcription of pro-apoptotic genes (BAX, PUMA, NOXA)
- Mitochondrial Pathway: BAX/BAK activation; mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization
- Caspase Cascade: Cytochrome c release; caspase-9 and caspase-3 activation
- Cell Death: Apoptotic cell death and clearance by immune system
- SASP Elimination: Removes source of inflammatory SASP factors
Tissue Rejuvenation
Functional Restoration
- Inflammation Reduction: Eliminates SASP-secreting cells; reduces chronic inflammation
- Stem Cell Activation: Removes senescence-induced stem cell dysfunction
- Tissue Remodeling: Allows healthy tissue regeneration
- Functional Improvement: Restores organ/tissue function (kidney, liver, muscle)
Research & Evidence
FOXO4-DRI's landmark 2017 Cell publication demonstrated dramatic rejuvenation effects in aged mice, establishing it as a leading senolytic candidate[4].
Aged Mouse Studies
Natural Aging Model
Key Findings: FOXO4-DRI treatment of naturally aged mice produced dramatic rejuvenation effects.
- Fur Regrowth: Restored dense fur in aged mice (visible rejuvenation)
- Kidney Function: Improved renal function markers; reduced fibrosis
- Exercise Capacity: Increased running distance and endurance
- Senescent Cell Clearance: Reduced senescent cell markers (p16, SA-β-gal)
- Safety: No apparent toxicity or adverse effects on healthy tissues
Chemotherapy-Induced Senescence
Accelerated Aging Model
- Model: Chemotherapy (doxorubicin) induces rapid senescence in mice
- FOXO4-DRI Treatment: Accelerated recovery from chemotherapy-induced damage
- Senescent Cell Elimination: Cleared chemotherapy-induced senescent cells
- Functional Recovery: Improved physical function and tissue health
- Clinical Relevance: Potential to mitigate chemotherapy side effects
Mechanism Validation
In Vitro & Molecular Studies
- Selective Killing: Induces apoptosis in senescent cells in vitro; spares proliferating cells
- FOXO4-p53 Disruption: Confirmed disruption of FOXO4-p53 interaction[8]
- p53 Transactivation Domain: Recent 2025 Nature Communications study identified disordered p53 TAD as target[8]
- p53 Activation: Demonstrated p53 nuclear translocation and target gene activation
- Apoptosis Markers: Confirmed caspase activation and apoptotic cell death
Pulmonary Fibrosis Applications (2022-2023)
Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Models
Research Findings: Multiple studies (2022-2023) have demonstrated FOXO4-DRI's efficacy in pulmonary fibrosis models[4][6]:
- Senescent Cell Clearance: Reduced senescent myofibroblasts in fibrotic lung tissue
- ECM Reduction: Decreased extracellular matrix production and deposition
- Fibrosis Amelioration: Improved lung function and reduced fibrotic markers
- Mechanism: Targets ECM-receptor interaction pathway; reduces TGF-β-induced myofibroblast senescence
- Comparison: Effects comparable or superior to standard antifibrotic medication (Pirfenidone)
Clinical Potential: Pulmonary fibrosis is a progressive, fatal condition with limited treatment options. FOXO4-DRI's ability to clear senescent fibroblasts suggests potential therapeutic application, though human trials are needed.
Reproductive Health Applications (2020-2024)
Age-Related Reproductive Dysfunction
Research Findings: Studies demonstrate FOXO4-DRI's effects on reproductive aging[2][7]:
- Testosterone Restoration (2020): Alleviated age-related testosterone secretion insufficiency by targeting senescent Leydig cells in aged mice[2]
- Spermatogenesis Improvement (2024): Improved spermatogenesis in aged mice through reducing SASP secretion from Leydig cells[7]
- Mechanism: Eliminates senescent Leydig cells; reduces senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)
- Outcomes: Increased sperm quality, improved testicular function, restored hormonal balance
Significance: Age-related decline in male reproductive function is a common concern. FOXO4-DRI's ability to restore testicular function suggests potential applications in reproductive medicine, though clinical validation is needed.
Cartilage & Chondrocyte Applications (2021)
Osteoarthritis & Cartilage Degeneration
Research Finding: FOXO4-DRI selectively removes senescent cells from in vitro expanded human chondrocytes[3]:
- Senescent Chondrocyte Clearance: Selectively eliminated senescent chondrocytes in culture
- Cartilage Health: Reduced senescent cell burden in expanded chondrocyte populations
- Clinical Relevance: Senescent chondrocytes contribute to osteoarthritis progression
- Potential Application: May improve outcomes in cartilage repair and osteoarthritis treatment
Keloid & Scarring Applications (2025)
Keloid Senescent Fibroblast Targeting
Recent Research (2025): FOXO4-DRI induces keloid senescent fibroblast apoptosis[10]:
- Keloid Fibroblasts: Promotes apoptosis of senescent fibroblasts in keloid tissue
- Mechanism: Promotes nuclear exclusion of upregulated p53-serine 15 phosphorylation
- Clinical Potential: Keloids are difficult-to-treat fibrotic scars; senolytic approach may offer new treatment strategy
Cancer Applications (2025)
Senescent Cancer Cell Targeting
Recent Research (2025): Peptide inhibitors targeting FOXO4-p53 interactions induce senescent cancer cell-specific apoptosis[9]:
- Selective Targeting: Induces apoptosis specifically in senescent cancer cells
- Mechanism: Based on p53 transactivation domain sequence; disrupts FOXO4-p53 binding
- Research Status: Early-stage investigation; requires further validation
Dosing & Administration
Research Dosing (Extrapolated from Animal Studies)
Subcutaneous Administration
Animal Study Protocol: 5 mg/kg IP, every other day for 3 doses (days 1, 3, 5)
- Human Equivalent Dose: ~0.8 mg/kg (for 70 kg person: ~56 mg per dose)
- Community Protocols: Vary widely; typically 10-50 mg per dose
- Frequency: Every other day for 3 doses (1 week cycle)
- Cycles: Single cycle; repeat after 3-6 months if desired
- Route: Subcutaneous injection (animal studies used IP)
- Timing: No specific timing requirements
Reconstitution & Storage
- Lyophilized Powder: Store at -20°C
- Reconstitution: Bacteriostatic water for injection
- Reconstituted Storage: Refrigerate at 2-8°C; use within 7 days
- Handling: Gently swirl; avoid vigorous shaking
Safety & Side Effects
FOXO4-DRI showed no apparent toxicity in animal studies, but human safety data is lacking[5].
Preclinical Safety
Animal Studies: No apparent toxicity or adverse effects in mice.
- No Toxicity: No adverse effects on healthy tissues in treated mice
- Selective Action: Targets senescent cells; spares healthy proliferating cells
- Organ Function: No adverse effects on liver, kidney, or other organ function
- Behavioral: No behavioral changes or distress in treated animals
Frequently Asked Questions
Clinical Trials & Development Status
FOXO4-DRI has strong preclinical data but no publicly reported human clinical trials as of current knowledge[6].
Preclinical Foundation
Animal Model Studies
Landmark 2017 Cell Publication: Established FOXO4-DRI as leading senolytic candidate.
- Natural Aging: Reversed multiple age-related dysfunctions in naturally aged mice
- Chemotherapy Model: Accelerated recovery from chemotherapy-induced senescence
- Mechanism Validation: Confirmed FOXO4-p53 disruption and selective senescent cell apoptosis
- Safety: No apparent toxicity in animal models
- Reproducibility: Effects replicated across multiple tissues and aging models
Path to Clinical Development
Challenges & Opportunities
- Peptide Delivery: Peptides face bioavailability challenges; may require optimization
- Dosing Translation: Animal-to-human dose translation requires careful pharmacokinetic studies
- Indication Selection: Multiple potential indications (aging, chemotherapy recovery, age-related diseases)
- Regulatory Path: Novel mechanism; regulatory pathway unclear
- Commercial Development: Requires significant investment for clinical trials
Community Interest
Longevity & Biohacking Communities
FOXO4-DRI has generated significant interest in longevity-focused communities due to dramatic animal study results. However, human use remains experimental and carries unknown risks without clinical trial data.
References & Scientific Citations
Research Integrity:
All references are verified publications from peer-reviewed journals with direct links to sources. FOXO4-DRI research spans from the original 2017 Cell publication through 2025, demonstrating ongoing scientific interest and validation.
Primary Research Citations
- Baar MP, Brandt RMC, Putavet DA, et al. Targeted apoptosis of senescent cells restores tissue homeostasis in response to chemotoxicity and aging. Cell. 2017;169(1):132-147.e16. [Cell] - PMID: 28340339 - Landmark original study - Established FOXO4-DRI as senolytic peptide
- Zhang C, Xie Y, Chen H, Lv L, Yao J, et al. FOXO4-DRI alleviates age-related testosterone secretion insufficiency by targeting senescent Leydig cells in aged mice. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(13):12729-12739. [PMC7053614] - PubMed - Cited by 98 - Reproductive aging application
- Huang Y, He Y, Makarcyzk MJ, Lin H. Senolytic Peptide FOXO4-DRI Selectively Removes Senescent Cells From in vitro Expanded Human Chondrocytes. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 2021;9:677576. [Frontiers] - DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.677576 - Cited by 50 - Cartilage/senescent chondrocyte study
- Han X, Yuan T, Zhang J, Shi Y, Li D, et al. FOXO4 peptide targets myofibroblast ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice through ECM-receptor interaction pathway. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2022;26(18):4867-4880. [Wiley] - DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17333 - Cited by 30 - Pulmonary fibrosis application
- Zhang R, Gao K, Sadremomtaz A, Ruiz-Moreno AJ. Identification of hotspots in synthetic peptide inhibitors of the FOXO4: p53 interaction. 2022. [Academia.edu PDF] - Cited by 1 - Structural/mechanistic study
- Liu Y, Hou Q, Wang R, Liu Y, Cheng Z. FOXO4-D-Retro-Inverso targets extracellular matrix production in fibroblasts and ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 2023;396(8):1801-1813. [Springer] - DOI: 10.1007/s00210-023-02452-2 - Cited by 10 - Pulmonary fibrosis mechanism study
- Li Y, Zhang C, Cheng H, Lv LY, Zhu X, Ma M, et al. FOXO4-DRI improves spermatogenesis in aged mice through reducing senescence-associated secretory phenotype secretion from Leydig cells. Experimental Gerontology. 2024;188:112375. [ScienceDirect] - DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2024.112375 - Cited by 8 - Male reproductive health
- Bourgeois B, Spreitzer E, Platero-Rochart D, et al. The disordered p53 transactivation domain is the target of FOXO4 and the senolytic compound FOXO4-DRI. Nature Communications. 2025;16:60844. [Nature] - DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60844-9 - Cited by 2 - Recent 2025 mechanistic study
- Kang D, Lim Y, Ahn D, Lee J, et al. Peptide inhibitors targeting FOXO4-p53 interactions and inducing senescent cancer cell-specific apoptosis. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2025. [ACS Publications] - Cited by 1 - 2025 cancer application study
- Kong YX, Li ZS, Liu YB, Pan B, Fu X, Xiao R, et al. FOXO4-DRI induces keloid senescent fibroblast apoptosis by promoting nuclear exclusion of upregulated p53-serine 15 phosphorylation. Nature Communications Biology. 2025;8:7738. [Nature] - DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-07738-0 - Cited by 2 - 2025 keloid/scarring application
- Ross MJ, Baar MP. Targeted apoptosis of senescent cells restores tissue homeostasis in response to chemotoxicity and aging. Kidney International. 2017;92(5):1055-1057. [Kidney International] - Commentary on original Cell study
- Allison SJ. Ageing: targeting senescence-associated tissue damage. Nature Reviews Nephrology. 2017;13(8):449. [Nature Reviews] - Cited by 6 - Review commentary
Disclaimer:
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. The products offered are for in-vitro laboratory research use only. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat, or cure any medical condition, ailment, or disease. FOXO4-DRI is NOT approved for human use. All research cited is from preclinical studies only.
Third-Party Testing Results
All products undergo rigorous third-party HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) testing to verify purity and quality.
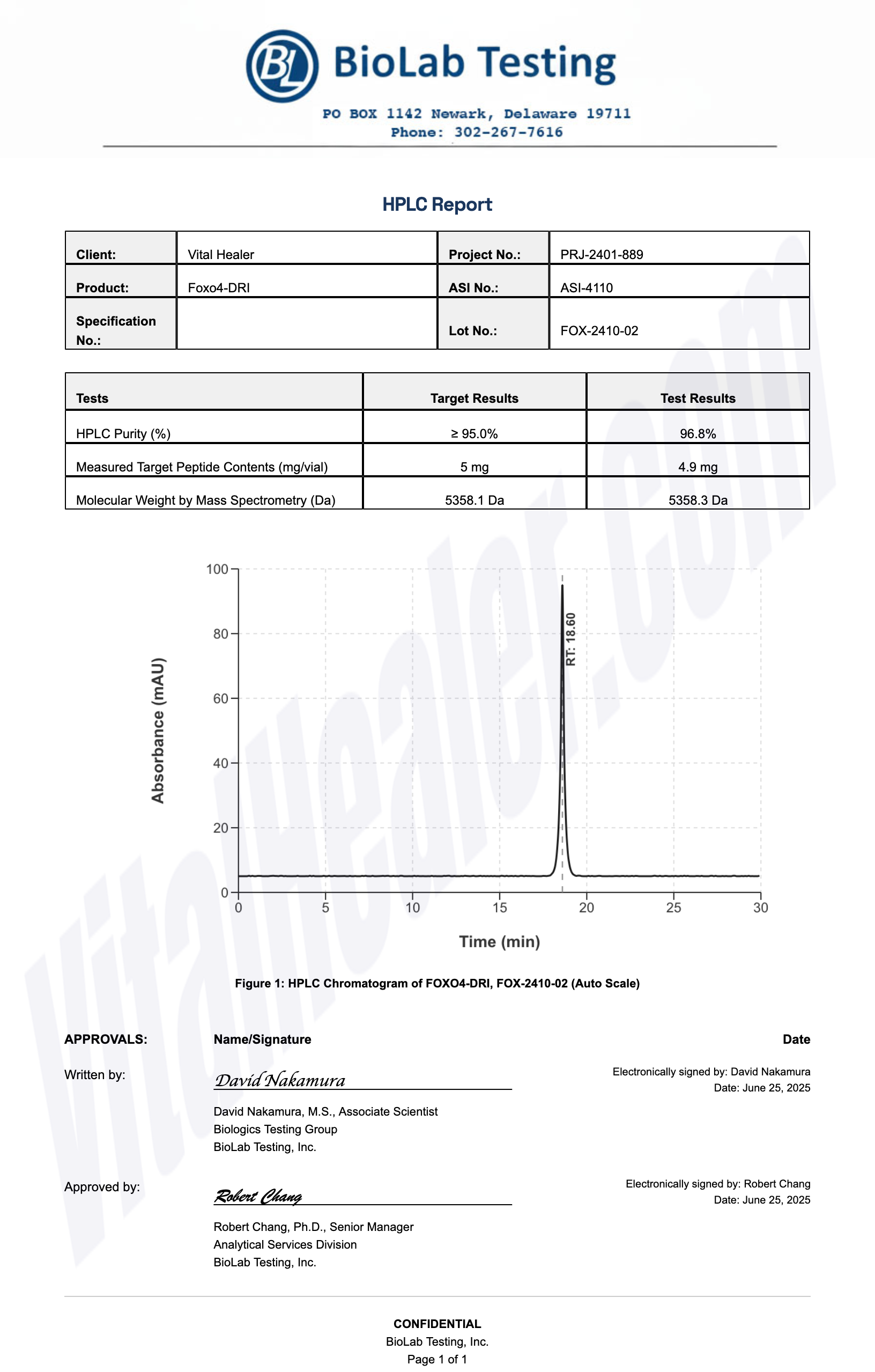
About HPLC Testing:
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a standard analytical technique used to verify peptide purity. Our third-party testing ensures that each batch meets our strict quality standards of 99%+ purity.
Related Research Peptides